User Experience Design
Have you ever been looking for a menu feature on a website and realized you can’t find it anywhere? Or have you ever been at a ticket machine and not been able to find the exact option you need? Then you know what the opposite of good user experience design is (UX design). But what is UX design, why is it so important, and what is the difference between UX and UI (user interface)?
Our guide provides the answers including basic information about user experience as well as some examples of successful UX designs.
What is 'user experience' and what is 'user experience design'?
The term 'user experience' has been a major topic among web designers for quite some time. However, there is often a lack of clear definition. To give readers the best possible experience on your website, you first need to know what good user experience design is and what user experience (UX) is. UX describes the entirety: a user’s emotional experience when dealing with a website, app, or any other technical product. UX design is characterized by knowledge of the website/app’s target group and what they require, as well as an attractive user interface, while still being goal-oriented and functional at the same time.
The Roman architect, Marcus Vitruvius Pollio, knew which components a product should have in order to provide a good user experience as early on as the 1st century BC. At that time, he described the three concepts of 'Firmitas' (strength), 'Utilitas' (utility), and 'Venustas' (beauty) as the basics of a good user experience design – without using the term itself, of course. This principle also applies more than 2,000 years later – whether you want to launch a website, create an app, or program a video game.
Three factors for a good user experience
1. In first place is ‘strength,’ or expressed in a more modern way, 'functionality'. Simply put, this means that your product must work. Crashes, downtimes, and long loading times are not part of a good user experience! The user must be able to rely on your product. If you can’t fulfill these requirements, the user will look elsewhere and it won’t be difficult to find an alternative thanks to the wide range of possibilities provided by today’s internet. If your product doesn’t work or doesn’t work as intended, the target group will not receive any word-of-mouth recommendations or positive reviews on the relevant App Store, meaning that your site will not be shared or linked to. 2. The next thing is utility: your website or app must offer the user value. This could be the products in an online store that the user would like to have, for example. Good content, whether informative or entertaining, is required on other websites. The general rules for good content apply here. How you can go about optimizing your content is shown in this article. In addition, this also means the site must be easy to use: the menu navigation must be intuitive, logical, and easy to remember. The functional range must correspond to the target group’s requirements, be up-to-date, and ideally be able to adapt to the user’s behavior and habits. Two examples of how not to do it: a graphic program that has its cropping function hidden in three sub menus and does not offer shortcuts is useless for the target group. Also, a writing program whose bold, underlining, and italic features are hard to find, won’t impress the reader since it doesn’t provide a good user experience. 3. Beauty is also needed for a good user experience, so make sure you don’t neglect the aesthetic! This area is where the most pitfalls have the possibility of occurring. The aesthetic scale can vary greatly depending on the cultural area, scene, or target group. Inconsistency, overloading, or using a design that misses the mark with your target group will discourage the user. Therefore, the design must not only be functional but also relevant to the target group.
UX vs. UI: what is the difference?
Sometimes user experience (UX) is confused with user interface (UI). Even though both terms are closely related, there are significant differences between the two: while user experience refers to the internal experience a user has as they interact with a company’s products and services, the term user interface refers to visual elements e.g. like buttons and icons. The latter encompasses the user interface on which user and machine interact and is the more technical term, while UX is the more strategic term. The user experience design is the result of a good user interface, but also includes areas such as information architecture, usability, or purely aesthetic aspects. Thus, user experience is an overarching term, whereas user interface, on the other hand, is a discipline.
User experience design in practice: how to create an authentic user experience
Putting theory aside for a moment – how does good user experience design look in practice? Firstly, ask yourself what your company or offer is: do you already have a corporate identity or important design guidelines in a style guide? If so, use this as the basis for any further steps. You will most likely benefit from the work that has already been previously done. This will ensure a consistent and professional appearance across all your communication channels. This enables you to be recognized by your users and eliminates the risk of design faux pas later on. For the next step, you should ask yourself - Who exactly it is that you intend to reach with your site or app? What are your target group’s wishes and demands? What do they expect from your offer? UX design is always tailored to a specific target group. This is the only way to provide the perfect experience for your visitors and users. For example, a gothic band’s website should be quite different from that of a porcelain factory. Accordingly, user experience design only works for certain target groups whose taste you should know in advance. This requires tests, surveys, and even large-scale target group studies so you can use the results to create personas. Concentrate on the essentials: an overloaded design is not helpful and will end up being distracting and irritating. A good user experience design, on the other hand, is minimal, simple, and clear. When it comes to websites, it’s important to regularly include blank spaces to give the user time to process content. If the design is too intense, the user will quickly become overwhelmed. There should also be a sufficient gap between the text, image, and any navigational elements, but make sure you also aren’t simply wasting space. Coordinate colors, fonts, and the layout of your content. Avoid stylistic inconsistency for your UX design. It can quickly overwhelm users if they are constantly confronted with new color schemes or fonts. In addition, lack of consistency in user experience design makes it look unclear. The taste of the target group is always important in this case. Once all aesthetic aspects are classified, the focus is on optimizing accessibility and user friendliness: a good user experience design does not have long loading times and leads the user quickly to their goal without sending them on several detours. Complicated menus should, therefore, be avoided. You should instead design an intuitive and easy-to-follow path to help the user get familiar with your software or website. Inexperienced users sometimes fail at basic intersections – despite all the optimization efforts to produce a chic UX design. Such users must be able to quickly find not only the most important functions but also be able to find support if necessary. For this purpose, you could provide a central help button. This could lead users, for example, through the application in a clear step-by-step fashion, or lead them directly to a searchable encyclopedia that explains all important terms and functions. To improve user experience even more, you could consider including a forum, contact form, or even a hotline for telephone inquiries.
Keep your UX design consistent and clear. All important functions must be easy to find and accessible. The key factors for a good user experience design are: smooth functionality, usefulness, user friendliness, and aesthetics.
User experience design: continuous optimization is required
The aim of user experience design is to enable the target group to have the best possible experience at any time. This means that the website or software must be continually improved in order to keep up with the progressive requirements of the target group. A simple example: a few years ago, classic website design was enough. But nowadays, your website will lose important users and possibly not make a profit if it doesn’t have responsive design for mobile devices or native apps for iOS and Android devices. Users might decide to use your competition’s website if their user experience is better. In this article, we explain how to make your website mobile.
Obtaining user feedback and studying the target group
Regular feedback is necessary if you want your UX design to be up-to-date and stay that way. Although you can detect and correct many inconsistencies by carrying out your own tests, the problem with internal testing is that there’s a risk of operational blindness. This means that you won’t see your own errors. So, for this reason, it’s highly advisable to collect independent opinions through user surveys and tests. For example, you should try to reward the target group with relevant non-cash prizes, free trial versions of your premium offer, or in-game items for all participants. There are many incentives to get feedback from (potential) users.
Even if your app is found in the Google Play Store or Apple App Store, it’s not always easy to share it with users. Dissatisfied users are more likely to give feedback than satisfied ones and will let you know immediately if something is wrong with your product or service – this can be a curse and a blessing at the same time. On one hand, feedback is important for being able to continue optimizing the user experience; on the other hand, many negative responses can quickly damage your reputation. If possible, react quickly to the criticism and offer help. Preferably, you have already carried out extensive (and independent) UX tests in the run-up to the launch and have already minimized the risk. It’s also a good idea to send out public messages to explain that bugs were fixed as this will calm many users.
If you have a forum and/or social media account for your offer, this is a great opportunity to keep users and prospects up to date. Sending news notifications regarding development updates, discovered bugs, or informing users that you’re optimizing your user experience design, will be gladly received. They bind the users to your offer and at the same time give them the opportunity to react to the changes. Last, but not least, a good and transparent information policy increases the user experience in the long-term.
UX design: measurements via eye-tracking
Costly, but very promising are complex UX measurements e.g. via heatmap analyses – the heatmap enables you to visualize a website’s usability. A proven technique for creating heatmaps is eye tracking. This technique uses special glasses, webcams, and external remote eye trackers to record the user’s behavior, focus, and perception. The obtained data can be used to optimize the user experience design e.g. if you notice users getting increasingly lost while looking for a certain function, you can use this information to improve user experience and adapt the design.
It’s worth making the effort for good UX design
Are you wondering if all the effort and cost for optimizing user experience is really worth it? These time-consuming and cost-intensive test phases are needed before software or websites are launched. The reasons for investing time and money into successful user experience design are numerous and clear:
- UX design puts the user first.
- It means the design of the website/app has an objectively measurable basis: the satisfaction of the user.
- It promotes goal-oriented work in the team.
- If you work directly with a functioning and up-to-date user experience design, you will later save development costs for corrections, support, and customer service.
- Continuous testing and optimization of the user experience leads to innovative and up-to-date designs. This puts you ahead of the competition.
- Aesthetically appealing designs attract attention and encourage users to continue to engage with your site or app.
- If users are familiar with the application, your offer will stay in their memory for longer – this will strengthen your brand.
- A high level of customer and user satisfaction connects users, generates likes and/or recommendations, and ultimately increases the conversion rate.
User experience design: best practice examples
In order to give users an authentic experience on a website or with software, creativity as well as functionality is required: otherwise your project won’t prosper. If long loading times are unavoidable on an app or a complex website, why don’t you turn them into part of the user experience design? Keep the user in the loop by explaining why the site is taking a while to load: this improves the user experience. The following examples show how to create real experiences with innovations and creativity:
The website of ParaNorman – making loading time fun
The website of the animation film, ParaNorman is an example of great user experience design, which solves this problem in an inventive way. A skeleton hand can be seen, impatiently drumming his fingers to sarcastically demonstrate that the site’s images are taking a while to load. This should lighten the user’s mood and make the wait less annoying. The actual site is also set out similarly: the user scrolls through the interactive website and gets to know the main character and the movie.
Wikiwand – Wikipedia redesigned
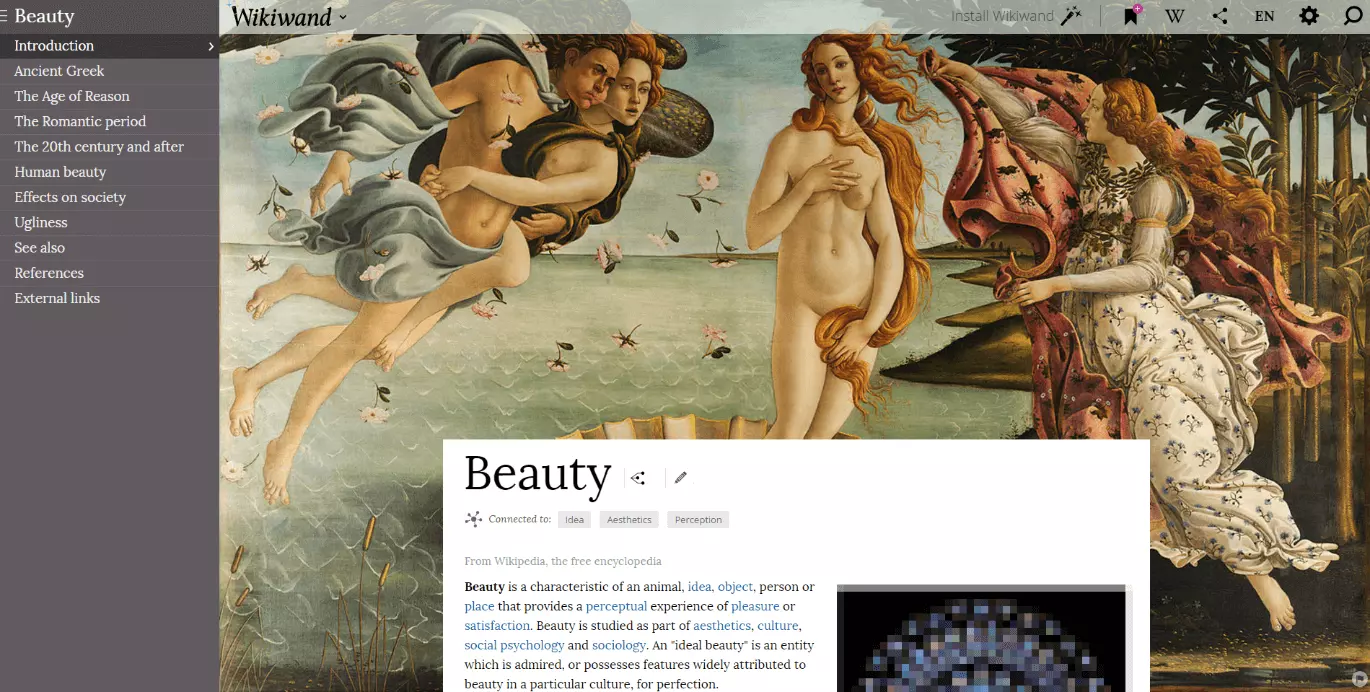
Wikipedia is great: the online encyclopedia provides several million articles in over 280 languages – an entirely unique web project. Even platforms with such popularity and reputation can be improved by a modern user experience design, which was proven by it being the Webby winner in 2015 for best user experience: the software, Wikiwand, can be downloaded as an app on smartphones and tablets, or installed as a browser plugin on stationary devices. It far surpasses the regular Wikipedia site with its modern design.
But why was this needed? Wikipedia has always worked smoothly and offers abundant information on pretty much any topic you can think of. Well, depending on the article, many entries are just long bodies of text with few or no images, making for a monotonous experience. Wikiwand does not modify Wikipedia’s texts, but changes the informational architecture: on the left side, the table of contents allows for faster navigation and orientation. This makes it easier for users to keep an overview when reading long and complex articles since the table stays visible as you scroll down the article.
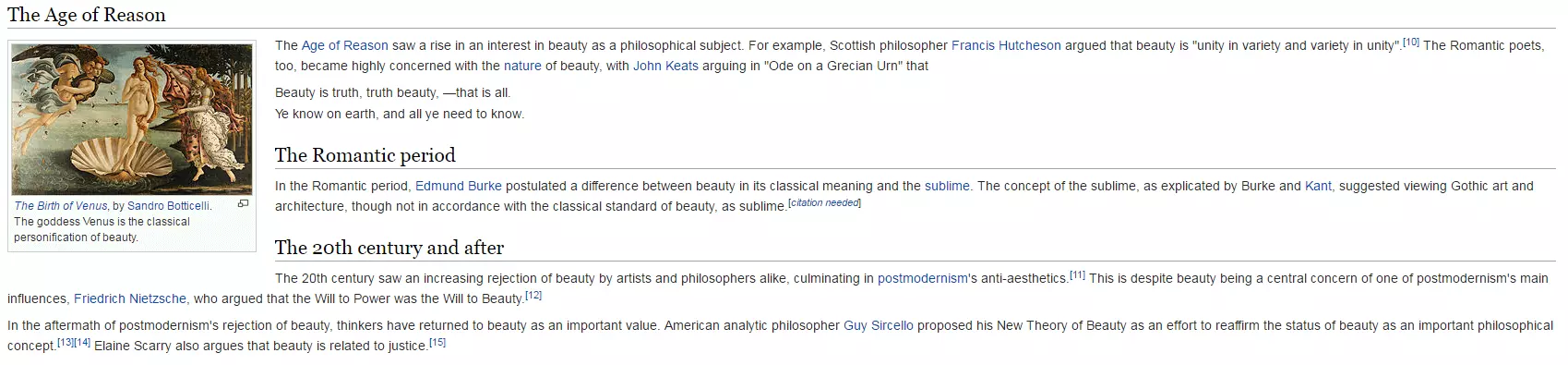
By making the images more prominent, the layout becomes a bit more relaxed. Some particularly expressive illustrations are used in the background e.g. this page has Sandro Botticelli’s painting 'The Birth of Venus' as the backdrop.
On the original page from Wikipedia, the same image appears further down and significantly smaller. Its significance is somewhat reduced, compared to it being used as the background where it immediately catches the reader’s attention and elevates the mood of the article. Don’t forget the educational value of this: even when you skim the text, you can’t miss the masterpiece behind it.
This is all thanks to one image – the background image. This also applies to hundreds of other example articles: an article about tigers using the animal as a background picture, or an article on different oceans having a corresponding photo. It seems that a picture is indeed worth a thousand words.