RAID level: the most important RAID concepts compared
Combining hard drives as a RAID has various advantages and disadvantages. These cannot be generalized since the specific properties of a network depend on the selected RAID level. Each level is different, depending on how many hard disks are combined and which methods are used to store the files.
A RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a combination of two or more storage media to form a single large logical drive. The specific function is determined by the respective RAID which is known as a RAID level.
We explain how RAID levels differ and what the effects of the different approaches are. Our comparison of RAID levels also shows how each performs in terms of cost, reliability, and performance.
RAID levels: an overview of the most important differences
RAID levels such as RAID 5 or RAID 6 describe different approaches for connecting hard disks in a network that functions as a single logical drive. When RAID technology was first presented in 1988, the idea was to save costs by combining disks in a hardware cluster. Today, the cost factor barely plays a role and is only considered when evaluating between the various levels.
The decisive properties in which RAID levels differ from one another today are as follows:
- Degree of resilience
- Read speed (output rate)
- Write speed (input rate)
- Utilization of available storage capacities
- Minimum number of hard drives required
It is often wrongly assumed that the individual RAID levels are based on one another, which is not true. However, there are combinations of two different levels such as RAID 10, which combine two basic levels: RAID 1 + RAID 0.
How do the different properties of the RAID level come about?
The primary goal of RAIDs is to increase the security of stored data. Failures of individual hard drives are compensated for and data loss is avoided. To this end, individual RAID levels employ different techniques to store files redundantly. The classic procedure is, for example, the mirroring of all data whereby information is duplicated in a disk cluster. Alternatively, other RAID levels rely on parity information that is stored together with the user data on the integrated data carriers and – in case of a defective storage medium – helps to restore data quickly and easily.
A RAID is not an alternative for a backup. The spatial and temporal separation of stored files that is at the heart of classic backups is not given in RAID networks!
To boost performance, many RAID levels make use of striping, a process whereby the stored data is broken down into strips and distributed evenly across all integrated hard drives. In this way, both the write and read speed can be optimized – the degree of increased performance depends on the chosen redundancy method.
Compared to individual drives, many RAID levels offer both increased reliability and improved performance. However, the following rule of thumb applies: the higher the fail-safety of a network, the weaker its performance improvement.
The maximum storage capacity users have available for their data depends on the methods used for redundancy. RAID levels that rely on mirroring data only have 50 percent of storage space available. Where parity is used in a RAID, the storage capacity increases with the number of hard disks.
Tabular comparison of the most important RAID levels
The relationship between fail-safety, performance, storage capacity and ultimately also the cost differs from one RAID level to the next. Some approaches such as RAID 0 and RAID 1 are designed for a single purpose. While RAID 0 ensures increased data throughput when reading and writing, RAID 1 focuses on the duplicate storage of files and thus only a minimal improvement in read speed is achieved (with a suitable RAID controller).
The table below compares the properties, strengths, and weaknesses of common RAID levels.
| RAID 0 | RAID 1 | RAID 5 | RAID 6 | RAID 10 (1+0) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum number of hard disks | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Process | Striping | Mirroring | Striping and Parity | Striping and double parity | Striping of mirrored data |
| Fail-safety | Low | Very high; single hard disk can fail | Medium; single hard disk can fail | High; two hard disks can fail | Very high; Failure of one drive per sub-array possible |
| Storage capacity for user data | 100 percent | 50 percent | 67 percent (increases with each added hard disk) | 50 percent (increases with each added hard disk) | 50 percent |
| Write speed | Very high | Low | Medium | Low | Medium |
| Read speed | Very high | Medium | High | High | Very high |
| Costs | Low | Very high | Medium | High | Very high |
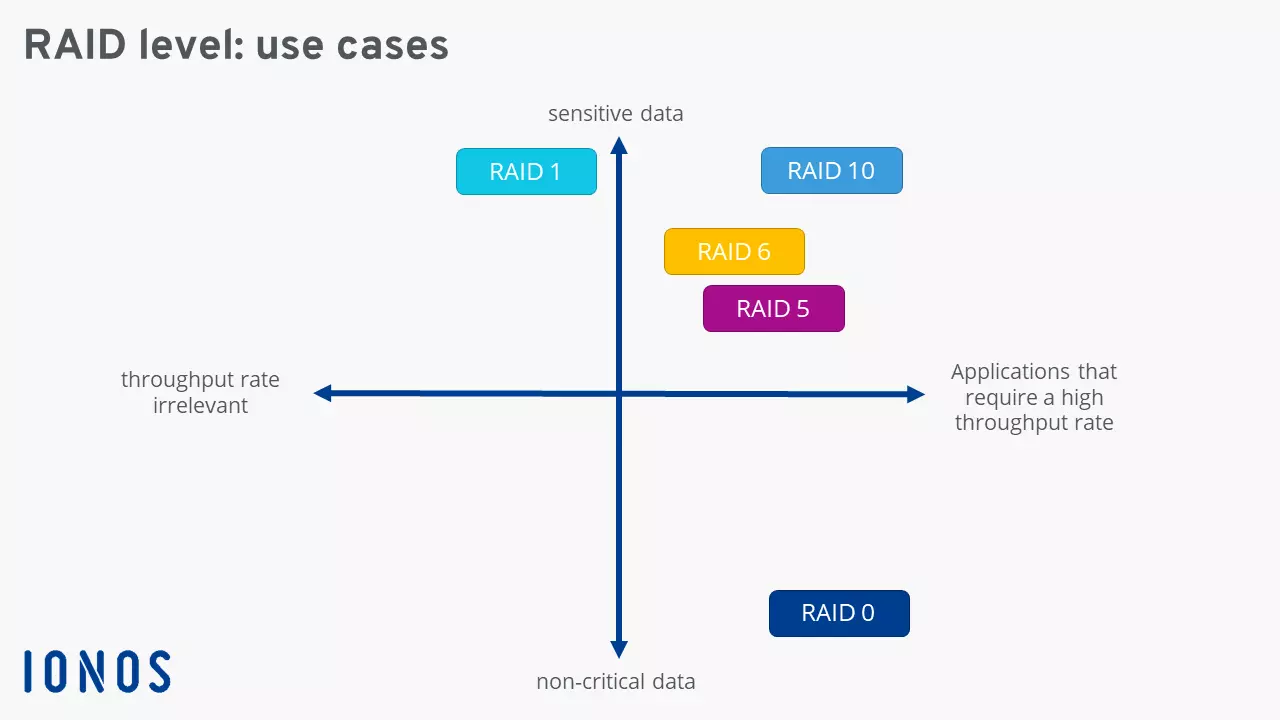
What are the different RAID levels used for?
Given their different properties, the RAID levels are suitable for a wide variety of applications. Because of a complete lack of redundancy, RAID 0 should be disregarded if you’re looking for a solution to store sensitive data. The network makes for a suitable SSD alternative for non-critical applications such as video and image processing software.
Expensive RAID levels 1 and 10, like many RAID networks, are not suitable for storing huge amounts of data. However, their high fail-safety is great for storing sensitive data. The two concepts are particularly advantageous for applications that require a high data throughput rate. File and web servers (RAID 1) or database and application servers (RAID 10) are typical application scenarios here.
RAID 5 and RAID 6 which work with parity are suitable to store smaller files, since the write speed is relatively slow. Database and transaction servers are typical use cases.
What storage alternatives exist?
For many years, RAID systems were the ultimate in saving data in a more fail-safe and performance-boosting manner. However, plenty of alternative technologies now exist.
Multi-copy Mirroring (MCM)
Multi-copy mirroring is a practical RAID alternative whereby – as with mirroring in RAID level 1 – several identical copies of the data are created. In contrast to a RAID system, however, these copies are on different hosts in the network and include a mode that continuously checks the status of the data. If this recovery mechanism encounters damage or inaccessible data, it is immediately repaired using a copy. The number of copies is determined by the user, with each copy always taking up as much storage space as the original, which makes MCM a rather expensive proposition.
Erasure Codes (EC)
Erasure Codes use algorithms that break down data into subsets or blocks – just like the striping method as in RAID levels 0 or 5. The individual data parts can be conveniently distributed to separate storage locations. Erasure codes also have a checking mechanism that ensures the readability and availability of the data. The RAID alternative requires additional storage space of 33 percent, which makes it one of the most cost-effective options for file backup. Erasure codes are best suited to storing large data sets, as the division into blocks is particularly efficient here.
Cloud backup
We’ve already touched on the fact that a RAID should never be used as an alternative to a backup and similarly a backup shouldn’t be misunderstood as an alternative to a RAID. Backups in the cloud serve the sole purpose of storing data in a separate location. Improving reliability or read or write speeds aren’t the aim of cloud storage. However, as long as hardware optimization isn’t your goal, cloud backup solutions are a good option for securely storing your data.
Cloud Backup from IONOS encrypts and safely stores your smartphone and PC data in certified IONOS data centers.