What is RAID 5?
Want to combine hard disks to form a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks)? Then you’ve got a few different options. One of the most common levels is RAID 5. This combination of three or more data carriers is characterized by a good balance between high performance and security, and costs. So, what makes RAID 5 a good level in terms of its price-performance, and how does it work?
What is RAID 5?
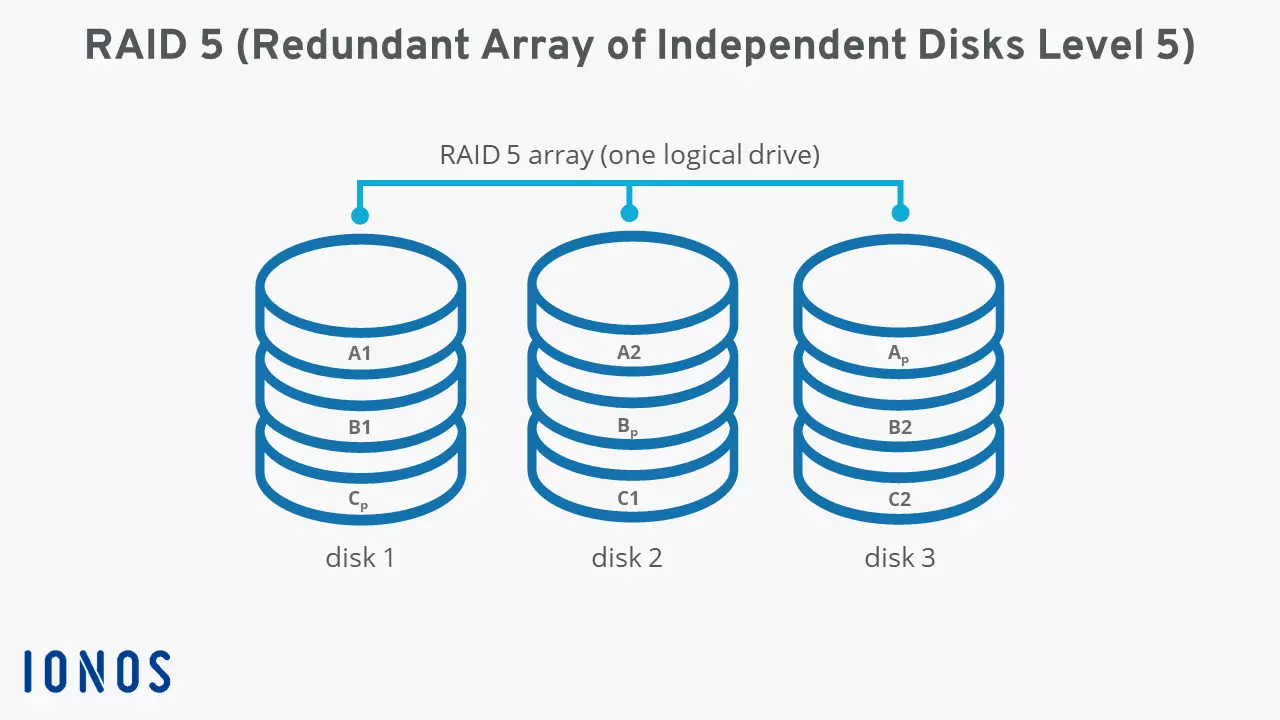
RAID 5 is a combination of three or more hard disks that function as a single logical drive and thereby outperform individual data carriers in terms of reliability and read speed. But to offer these advantages, a RAID 5 system relies on two active methods. On the one hand, the network must distribute files evenly over all clamped disks, which is also known as “striping”. On the other hand, a RAID 5 calculates parity information for all stored data, which is also distributed to the various storage media. Using a XOR link, the storage system then enables the reconstruction of lost or damaged data blocks.
XOR stands for eXclusive OR. A XOR link connects two statements via the two-digit junction of the same name “exclusive or” or “either ... or”. For data in a RAID 5 network, this means the following: all individual elements of a data strip, which are evenly distributed on the hard drives, are linked to the appropriate parity information using XOR logic. When devices access the data record, they can either read the exemplary data “A1” on hard disk 1 directly from the disk or reconstruct it using the parity block “Ap”.
The total capacity a RAID 5 system offers for user data can be calculated using the following formula:
(Number of hard drives - 1) x storage capacity of the smallest hard driveFor three storage media with 1 terabyte (TB) each, this results in a capacity of 2 terabytes. The remaining 1 terabyte is blocked for parity information. Regardless of the total storage size, a RAID 5 is only at risk if at least two hard drives fail simultaneously. That’s why, typically, an odd number of data carriers, i.e., three, five, seven, etc., is combined.
A RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a combination of at least two different storage media to form a single large logical drive. The specific function is determined by the respective hard drive setups, which are defined in RAID levels such as RAID 5. Its key advantages are enhanced data security and an improved data throughput rate.
An overview of the functionality of RAID 5
Striping and parity are the decisive features of RAID 5. What makes the RAID level special is the combination of drives and that the system distributes user data and parity information to all integrated hard drives. For example, RAID 4 combines both methods, but saves the parity blocks on a dedicated disk.
To make the functional principle of RAID 5 more tangible, the following diagram illustrates the data storage in a system using three hard drives as an example.
The advantages and disadvantages of RAID 5 systems
RAID 5 is characterized by a good price-performance ratio due to its efficient generation of redundancy. In contrast to other systems, the files are not saved in multiple versions, but only redundantly thanks to the parity blocks. Compared to use of individual drives, the storage capacity decreases, but RAID 5 networks retain a comparatively large chunk of the original capacity. On the other hand, RAID 5 is a cost-effective solution to boost read speed. The striping of the data allows parallel access to several parts of a related data block, so that inquiring devices can complete the read process much faster.
Another strength of RAID 5 is increased reliability. If a hard disk fails because it is defective, or if the data on a disk is lost for other reasons, operations can still be maintained. Since the remaining storage media are used more heavily during the recovery process, the risk of failure increases significantly during this period.
However, RAID 5 is not without its disadvantages. Each write process to the hard disk cluster is connected with an additional read step in order to check and recalculate the parity information that is available. Another step is needed to distribute the parity data for the newly stored user data on the disks. Compared to the individual drives and other RAID levels such as RAID 0, the write speed of the data carriers in a RAID 5 system is much lower.
| Advantages of RAID 5 | Disadvantages of RAID 5 |
|---|---|
| Increased reliability through parity | Write speed reduced compared to single drives |
| Good price-performance ratio in terms of redundancy and storage optimization | The storage capacity of the individual hard drives is somewhat limited |
What are typical usage scenarios for RAID 5?
RAID level 5 offers a good compromise between cost and performance optimization compared to separate hard drives. The network also scores high for reliability. However, the reduced write rate means the storage solution is of little interest for databases with multiple larger files. In other words: RAID 5 is best used for applications that access multiple small file blocks. Typical application scenarios of RAID 5 therefore include servers for microtransactions and database servers, which can contain a large number of entries, but are clearly limited in terms of maximum file size.
A RAID 5 is not a backup solution! If more than one hard disk fails, most of the data can no longer be restored – only the smallest files remain intact on a disk.
What other common RAID levels are there?
Data redundancy with parity, which is what makes RAID 5 so efficient, isn’t unique to the level. RAID 6 also relies on the principle and even distributes the parity information twice to the integrated data carriers. Levels RAID 1 and RAID 10 take a different approach. Here, data is fully mirrored, which means that these systems offer one hundred percent redundancy. RAID 0 only increases the speed with striping and offers no redundancy at all.
A detailed comparison of the various systems can be found in our comprehensive RAID level comparison.
Want a reliable cloud solution to secure your devices and data? Cloud Backup from IONOS encrypts and stores your data in certified IONOS data centers!