Server failure: risks, consequences, countermeasures
When it comes to online crime, businesses think primarily of economic espionage, stealing sensitive business data, and violating data protection. But increasing digitalization has meant that online attacks have attained and new level. More and more businesses depend on IT systems that link companies to public networks and provide hackers with opportunities to attack. If a cyber attack causes system failure, this could lead to interruptions that can prove costly. It only takes a few minutes for server failure to cause thousands of dollars’ worth of damage. Companies that could experience especially large losses are those whose servers host shopping software or provide a central database. However, server failures aren’t just caused by external sources; internal risks can also threaten the operation.
In addition to protecting against external threats and the standard procedures relating to disaster recovery, a solid security concept also includes organizational and staffing measures. Countermeasures are generally based on compensation: technically, this is based on providing redundant hardware within the context of high availability, or to bypass downtime with stand-by systems. Data security can be ensured by backup and recovery software as well as by redundant memory architectures. The financial consequences of server failure can potentially be covered by insurance.
Failure scenarios at a glance
Security experts differentiate the causes of server failure between internal and external threats. Internal threats include all scenarios where failures are caused by a company’s own IT infrastructure, utilities, or employee error. External threats, on the other hand, are deliberate external attacks or unpredictable events such as accidents or disasters.
Internal hazards:
- Fire in the computer center
- Power outage in the computer center
- Hardware failure (hard drive crash, overload, overheating)
- Software error (database failure)
- Network issues
- Human error
External hazards:
- Infiltration (man-in-the-middle attack, phishing, social engineering)
- Sabotage (attacks on SCADA systems)
- Viruses, Trojans, and worms
- Distributed denial of service attack (DDoS)
- Hardware theft
- Natural disasters (earthquakes, lightning, flooding)
- Accidents (plane crash)
- Attacks
As a rule, companies find it easier to prepare for internal security risks than external threats. The reason for this is that hackers always adapt their attack patterns to current security standards and continually attack corporate networks with new malicious programs or infiltration strategies. Companies can reduce the risk of internal dangers, on the other hand, through an uninterrupted power supply, fire protection measures, highly available servers, and comprehensive security training.
Consequences of system failure
The financial cost of server failure depends on several factors and also what kind of server is down; an e-mail server, web server, analytics server? How long the server was down also plays a part. If it was only a few minutes, it might not be worth calculating the loss, but for longer amounts of time it might make sense to work it out. If the server was being used by employees, you need to work out how much the employees were paid to technically do nothing, which obviously depends on their salary. If the culprit is an e-commerce server, it makes sense to calculate how many orders couldn’t be placed during the time the server was down. To do this, look at the time period e.g. Wednesday 5-7pm and compare it with how many orders you normally receive during this time. If an e-mail server was down, the cost depends on how much your company relies on e-mail traffic. Customers may be annoyed that they didn’t receive quick answers to their queries if they’re used to doing so. This could be enough for some customers to stop using your service or buying your products.
Don’t forget the actual cost of fixing the server. It is of course always a good idea to have proper backups at the ready in case the server does go down.
Whether server failure causes service interruption and to what extent, depends on the respective industry and the business model. To waste as little money as possible, you could start on other tasks when a server failure prevents you from doing your regular work; call meetings, make phone calls, or bring customer meetings forward. If your central process relies entirely on IT this could prove a bit more difficult. It costs the company an exceptional amount of money if customers aren’t able to place orders, or the SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) system failure paralyzes the production line.
When calculating the cost of service interruption, in addition to taking into account the employees’ hourly salaries and losses due to fewer or no customer orders, you might also face contractual fines due to delays in delivery times. Your reputation could also be at risk, but it’s almost impossible to calculate such a factor.
Countermeasures
In order to counteract server failures, you need to implement some preventative measures. This usually refers to a series of infrastructural and organizational measures when selecting and designing the server room. A lot of helpful information on how to avoid as well as recover from server failure can be found on Oracle.
Fire protection and utilities
In order to prevent server failures due to physical influences such as fires, floods, power failures, or hardware sabotage, server rooms and data centers need to be configured accordingly. The first step is to decide where the server should be located. Basements are definitely not recommended since there’s the danger of them flooding during storms or natural disasters. In addition, access to the premises should be restricted to specialist personnel and be controlled by a security check. Server rooms are not recommended to be used as permanent workplaces.
Fire damage can possibly be prevented by installing fire protection and extinguishing systems. This includes installing fire protection doors, fire detection devices, hand-held fire extinguishers, and automatic fire extinguishing systems (e.g. gas extinguishing systems). Further preventative measures include fire protection requirements for storing combustible materials correctly, using fire-resistant sealing on cables, and using suitable insulation materials for thermal insulation or soundproofing.
Technical equipment converts electrical energy into heat. The temperature in the server room could rise due to the sun’s rays seeping in. In order to prevent server failures and data errors due to overheating and high humidity, you should use powerful ventilation and cooling systems. Optimal storage conditions for long-term storage media is a temperature of between 68°F and 72°F, and with 40% humidity.
The basic pre-requisite for smooth server operation is a constant power supply. Interruptions as small as 10ms can lead to IT malfunctions. It is possible to bridge supply gaps and longer-lasting failures by using standby generators. These enable you to have a self-sufficient operation that is independent of the public electricity network, thereby helping to avoid interruptions in the usual operation.
Failure safety
Medium-sized companies in particular underestimate the impact that IT interruptions have on business operations. A reason for this is the high reliability of standard components that are now used in corporate IT. Their availability is generally estimated to be 99.9%. This number might seem high, but if the system operates 24 hours daily for a year, this could result in a maximum downtime of almost 9 hours. If this ends up happening exactly during the peak sales period, a relatively short server failure could prove costly to the company. Highly-available IT systems with an availability of 99.99% are the standard now when it comes to supplying business-critical data and applications. In this case, a maximum downtime of 52 minutes per year is guaranteed. Some IT experts even believe 99.999% availability is possible, which would mean no more than 5 minutes of downtime annually. The problem with the information regarding availability is that it only refers to the reliability of server hardware. According to IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)’s definition, a system is highly-available if it can ensure the availability of its IT resources despite several server components failing. 'High Availability (HA for short) refers to the availability of resources in a computer system, in the wake of component failures in the system.' This is achieved, for example, by servers that are completely redundant. All operating components – especially processors, memory chips, and I/O units – are available twice. This prevents a defective component from paralyzing the server, but high-availability doesn’t protect against fire in the data center, targeted attacks by malicious software and DDoS attacks, sabotage or being taken over by hackers. When it comes to real operations, entrepreneurs should therefore expect significantly longer downtimes and take appropriate measures to prevent and limit damage. Other strategies to compensate for the failure of server resources in the data center are based on standby systems and high-availability clusters. Both approaches are based on networks of two or more servers, which together provide more hardware resources than are needed for normal operation. A standby system is a second server that is used to safeguard the primary system as soon as it fails due to a hardware or software error. This service takeover is known as failover and initiated automatically by cluster manager software without any administrator intervention. A structure like this, consisting of an active and passive server node can be considered as an asymmetric high availability cluster. If all nodes in the cluster provide services in normal operations, this is known as a symmetrical structure. Since a time delay occurs when a service is migrated from one server to another, short-term disruption to standby systems and high-availability clusters cannot be completely prevented.
Defense systems
To counter hackers’ damaging influence, administrators use various software and hardware solutions that should detect, avert, register, and deflect their attacks. In order to protect a server against unauthorized access, critical systems with firewalls and demilitarized zones are closed off from public networks.
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) enable automated monitoring of servers and networks, alerting users as soon as manual break-in attempts or automated attacks by malicious software are detected: a process based on pattern recognition and statistical analysis. If intrusion prevention systems (IPS) are used, automated countermeasures take place after the alert. It’s common to be connected to a firewall so that data packets can be discarded or suspicious connections can be interrupted.
In order to keep hackers away from business-critical IT systems, administrators also use honeypots. These appear to hackers as supposedly attractive targets that run isolated from the productive system and therefore have no influence on the system’s functionality. Honeypots are constantly monitored and enable admins to respond quickly to failures and are able to analyze attack patterns and strategies used.
Data backup and recovery
In order to be able to quickly restore business-critical data even in the event of server failure, it’s recommendable to develop a data protection concept in accordance with international industry standards such as ISO 27001. This regulates who is responsible for the data backup and names the decision makers who can provide data recovery. Furthermore, the data backup concept determines when backups have to be created, how many generations should be saved, which storage medium should be used, and whether specific transport modalities are required such as encryption. In addition, the type of data backup is defined:
- Full data backup: if all the data that you wish to back up is stored on an additional storage system at a certain time, this is referred to as a full data backup. Whether the data has changed since the last memory process is not taken into account in backups like these. A full data storage therefore takes a long time and has a high memory requirement, which is particularly important when several generations are stored parallel. This type of data backup boasts simple and fast data recovery since only the last memory state has to be reconstructed. However, companies lose this advantage when backups aren’t carried out regularly enough. If this is the case, a lot of effort is required to adapt subsequently modified files to the current state.
- Incremental data backup: if companies decide on an incremental backup, the backup includes only those files that have changed since the last backup. This reduces the time needed to perform a backup, as well as meaning that the memory requirements for different generations are also significantly lower than with full data storage. An incremental data backup requires at least one back-up generated by a full-data backup. In practice, therefore, there are often combinations of both storage strategies. Several incremental backups are generated between two full-size backups. When it comes to data recovery, the last full data backup is used as the basis and supplemented by the data from the incremental storage cycles. As a rule, several data backups must be aligned one after the other.
- Differential data backup: differential data backup is also based on full data protection. All data, which has changed since the last full data backup, is backed up. In contrast to the incremental data backup, these backups aren’t linked together. For data recovery, it’s enough to compare the last full data backup with the most recent differential backup.
The storage strategy used in the company depends on the availability you require as well as economical aspects. Central influencing factors are tolerable recovery times, the frequency and time of the data backup as well as the relationship between the change volume and the total data volumes. If the latter are almost identical, it’s possible to save memory by incremental or differential methods.
Training
Information security methods can only be established throughout the company if all employees recognize and accept that they are partly responsible for the company’s economic success. Security awareness can be raised and maintained if the company provides regular training courses, aimed at familiarizing employees with internal and external risks, and possible scenarios.
The basis of systematic training courses are the rules and regulations for handling security-relevant devices as well as a disaster recovery plan, which provides employees with instructions about which steps to take to restore normal operation as quickly as possible. A structured approach to creating appropriate concepts is provided by business continuity management.
Business continuity management (BCM)
In order to minimize damage caused by server failures, companies increasingly invest in preventative measures. The focus is on business continuity management (BCM). In the IT sector, BCM strategies are aimed at counteracting server failures in critical business areas, and ensuring immediate recovery if an interruption occurs. Business impact analysis (BIA) is the pre-requisite for appropriate emergency management. This helps companies identify critical business processes. A process is classed as critical when a server failure has a significant impact on operation. The BIA concentrates on the consequences of concrete damage scenarios. Causes of server failures, the probability that possible threats might occur, and countermeasures are recorded in the risk analysis. How BIA and risk analysis can be implemented methodologically within the framework of BCM is the substance of various standards and frameworks. The BSI Standard 100-4 is recommended as a detailed guide.
Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
The first step towards comprehensive business continuity management is the business impact analysis. Key questions regarding this analysis are: which systems are the most important in maintaining the core business? What does it mean for the operation if these systems fail? It is advisable to identify the company’s most important products and services as well as the underlying IT infrastructure. If a company primarily relies on internet sales, the servers that supply the online store and its associated databases definitely need to be protected. A call center, on the other hand, would classify its telephone system as critical for running its business. The BIA includes a prioritization of systems that are to be protected, a way of calculating losses, as well as informing which resources are required for system recovery.
Risk analysis
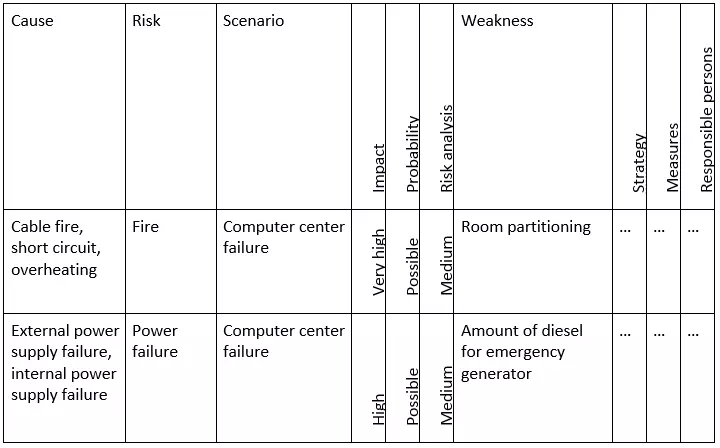
A risk analysis within the scope of emergency management enables you to identify internal and external risks that could cause a server to fail and consequently interrupt the operation. The aim is to make any security risks and their causes known and to develop appropriate countermeasures in order to reduce any potential danger. An assessment of the risks can be made on the basis of the expected damage and the likelihood that it will occur. An example of a risk classification is shown in the following example from the BSI Standard 100-4:
Recording the current state
If the risks and damage potential in a server failure scenario were determined within the framework of the BIA and risk analysis, the third step on the continuation strategy journey is to record the actual state. Emergency measures that have already been established as well as current recovery times are important for this step. Recording the actual state enables companies to estimate the need for action in case of serious security risks and their associated investment costs.
Selecting the continuation strategy
As a rule, there are various strategies for the different internal and external hazards, which allow the operation to continue running despite disruptions, or promise a speedy recovery at least. When it comes to business continuity management, it is, therefore the decision maker’s responsibility to decide on the continuation strategy to be used in an emergency. The decision is based on a cost-benefit analysis that includes key factors, such as which financial resources are required, how reliable the solution is, and the estimated recovery time.
There are several solutions available if you want to develop a continuation strategy to prevent a data center fire: minimal solutions include compensation for insurance paid out due to operational failures and a replacement center with a hosting service provider. It would be more costly to convert the existing server room so that it complies with modern fire protection standards. If larger investments are available, consequential damage can be reduced by building a second, redundant server room.
Already established continuation strategies are defined in the emergency safety concept, which contains specific instructions for all relevant emergency scenarios.