Secure network connections with IPsec
IP packages, the basic elements in internet data communication, are made up of two parts: user data like speech, text, or images, and header data containing, among others elements, the addresses of the sender and recipient. The biggest issue with these data packages, as they pass through various routers on their way to the recipient, is the fact that Internet Protocol doesn’t have encryption or authentication mechanisms. This means that data is transferred unencrypted from router to router and can be read or tampered with. And the three pillars of information security – confidentiality, authenticity, and integrity – are not guaranteed.
For this reason, the protocol suite Internet Protocol security, or IPsec for short, was developed in order to give the Internet Protocol vastly increased safety protection. Together, the two combine to ensure reliable security during data package transfers over open networks, which is why IPsec is an important building block for many VPN connections (virtual private network).
What is IPsec?
IPsec is a protocol suite, the architecture of which was suggested as a standard by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The IETF is an organization concerned with the technical advancement of the internet. IPsec was developed for the newest version of Internet Protocol (IPv6) and retrospectively also for IPv4. It can be divided into the following three function groups:
- Transfer protocols: Authentication Header (AH), Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
- Key management: Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP), Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
- Database: Security Association Database (SAD), Security Policy Database (SPD)
Through the two transfer protocols, AH and ESP, IPsec guarantees the authenticity and integrity of sent data, ensuring that content from the sender reaches the recipient without being altered. For this purpose, AH offers both data origin authentication, to confirm its legitimacy, and protection for the package during transfer. Additionally, the AH protocol assigns a sequence number to the header, protecting packages from potential repeated transfer.
The ESP protocol provides additional encryption for the data package alongside identity and integrity protection. But ESP authentication differs from that of the AH protocol in that it does not take the outer IP header into account. By using an additional encapsulation, however, the ESP content can be securely delivered across networks with address translation (NAT), which are typically used in private DSL connections. The IKE protocol is primarily responsible for managing ESP encryption. It negotiates the security associations between sender and recipient, uses the Diffie-Hellman algorithm for secure key exchange, and technically implements the definitions for the ISAKMP framework.
The necessary information for package transfer using IPsec is stored in the two local databases, SPD and SAD. The entries in the SPD, security policy database, determine which transmission protocol – AH, ESP, or both – is to be used for the secure connection. The SAD, security association database, manages the specific security association entries provided by the IKE protocol; giving the sender the encryption key and the receiver the corresponding decryption key.
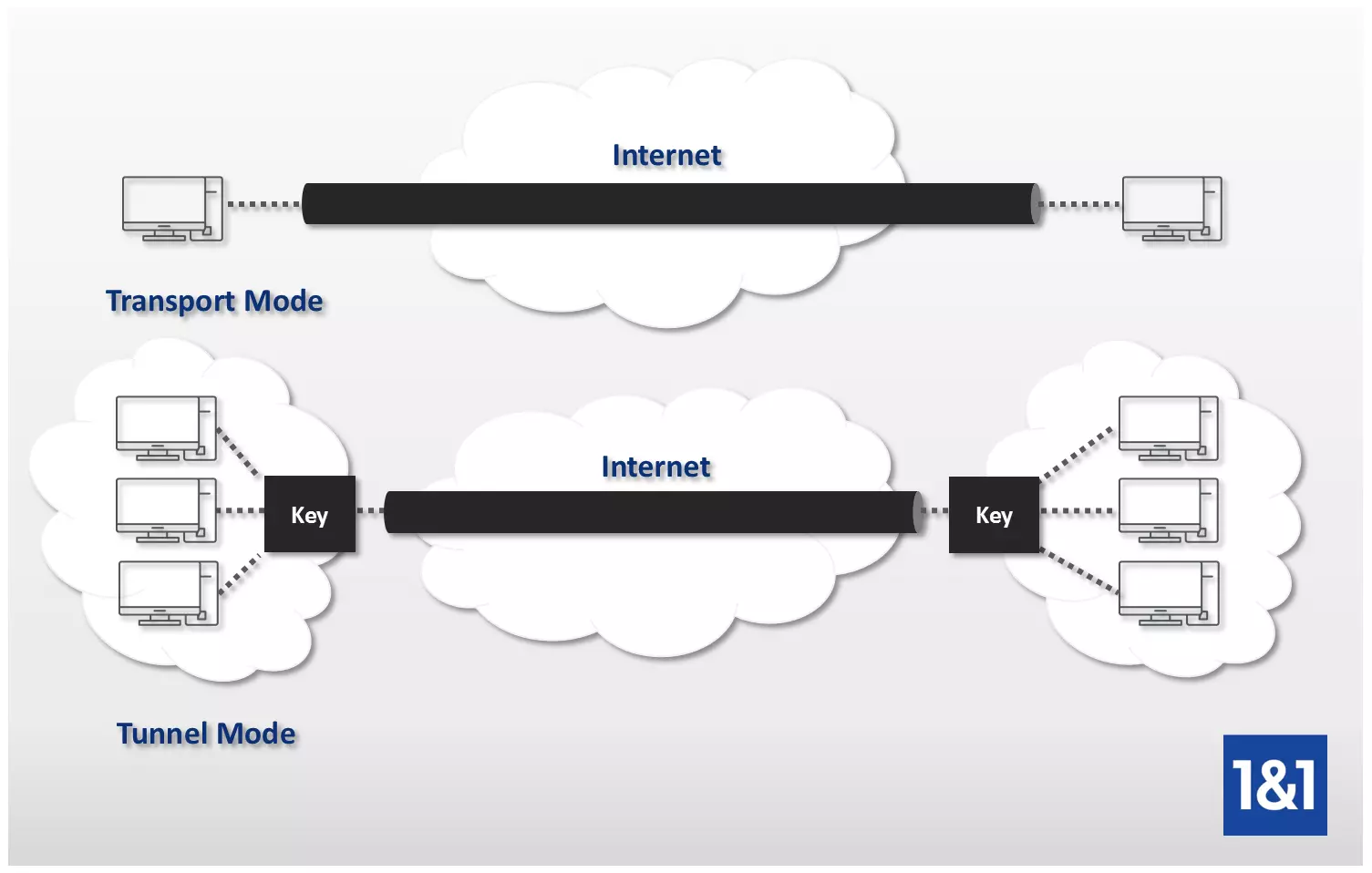
The two types of IPsec: Tunnel vs Transport
Transport mode
The following occurs when IPsec is used in transport mode: the header of the transmission protocol is inserted between the IP header of the data package, which remains untouched, and the user data. Protection begins from the sender and remains throughout the transfer until the target computer is reached. Only after the package has been received is the original user data released and made available to the recipient. This means that the cryptographic and communicative terminal points are identical. Transport mode has the advantage of a very quick processing time, but only secures the user data, while the source and target addresses remain unprotected. In practical use, this mode is common for host-to-host or host-to-router connections, e.g. for network management.
Tunnel mode
In tunnel mode, the data package receives a completely new IP header in which both the source and target address are hidden together with the user data. The header of the transfer protocol is also implemented – just as in transport mode. So it can be said that the original package is encapsulated as well. The new, outer IP header defines the cryptographic terminal point, which isn’t identical to the actual communications point stored in the inner IP header. Only once the package reaches this cryptographic end point, known as a security gateway, can it then be decrypted and forwarded on to the intended recipient. Data transfer in tunnel mode is typically carried out from gateway to gateway; host-to-gateway and host-to-host connections are also possible.
IPsec: strengths and weaknesses
When using VPNs, which are the most common application area of the protocol suite, IPsec has a decisive advantage over alternatives like SSL: it can be used independently from any application at network level. Once the connection is made, different forms of data, like e-mail, file transfer, or IP telephony can be sent without the need to install program-specific tools. This makes the protocol stack the most cost-effective solution for VPN connections. In turn, the use of IPsec for remote access requires special software that must be installed, set up, and maintained on each client individually. The application independence can also quickly lead to unauthorized access issues if not protected by a central firewall, as a breach would put all applications at risk.
But what’s undeniable is the performance and reliability of IPsec: if problems occur, another gateway can be opened effortlessly on a clustered system, while thousands of users are simultaneously supplied with data package. Lastly, thanks to its high security, IPsec is seen as the best solution for all sensitive data and for internal company traffic systems that don’t permit anonymous users.