E-business
E-business is short for “electronic business.” As an overarching term, it refers to any method of utilizing digital information and communication technologies to support or streamline business processes – from preparation to implementation. However, it can also refer more specifically to the business processes of online stores or other internet-based companies.
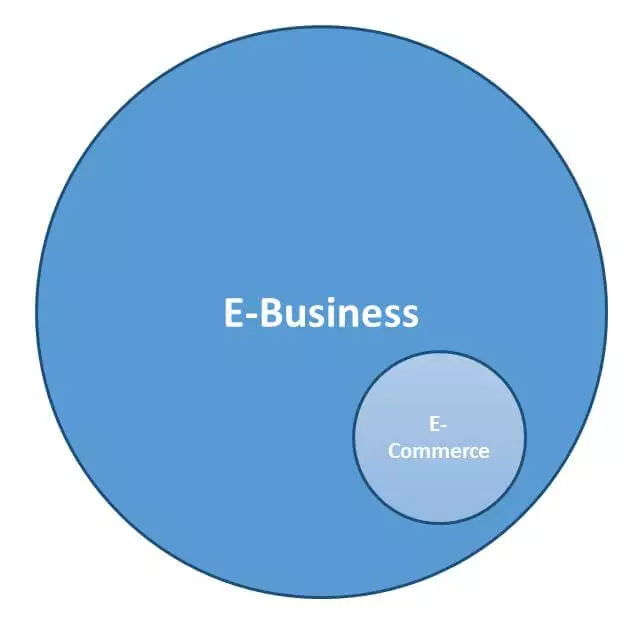
These two slightly different interpretations of the term have led to a problem: a widely accepted, precise definition of e-business does not yet exist. As a result, it’s interpreted broadly, and is commonly misunderstood – mainly in relation to e-commerce. Although there is some overlap, e-commerce refers to trading products and services online, and so is strictly only speaking of one aspect of e-business.
- Get started with stunning designs
- Grow with advanced marketing and admin tools
- Sell on social and online marketplaces
E-business is a general term that encompasses all forms of using digital information and communication technologies to support and optimize business processes. In contrast, e-commerce describes only the online trading of products and services, and is therefore only a subsection of e-business.
Improve your success on the Internet with the business hosting package from IONOS.
The word e-business became popular following an IBM advertising campaign about computerized procedures to automate business processes. On October 7th, 1997, the IT and consulting firm published an eight-page essay in the Wall Street Journal and used the term to describe how corporate systems would fundamentally change in the digital era.
At the time, IBM understood e-business as “redesigning strategic business processes and meeting the challenges of a new market increasingly characterized by globalization, and based on new knowledge.” Although the company wanted to present itself as an expert on this topic, they nevertheless decided against patenting the term in the hope that other companies would engage with the concept and help to form a new industry.
- Simple registration
- Premium TLDs at great prices
- 24/7 personal consultant included
- Free privacy protection for eligible domains
Components of electronic business
The core components of e-business are information, communication, and transaction. Business partners use digital networks (i.e. public or private communication networks) to conduct business processes using innovative technologies to improve efficiency. Three key areas are particularly important for e-business:
E-procurement: the electronic sourcing of products and services by companies, focused on reducing costs and effort.
Online stores: the electronic sale of products and services via appropriate platforms, such as online stores.
Online marketplaces: electronic commerce via digital networks, connecting the buyers and suppliers of products and services.
There are also two further areas of e-business:
Online communities: electronic communication network between individuals and organizations, which supports data and knowledge sharing as well as the preparation of transaction decisions.
Online companies: electronic business cooperation for connecting individual company services, resulting in a virtual business with a common transaction offer.
Features of e-business
To fully understand the concept of e-business, you must first grasp the link between e-business and the net economy and know who the typical market participants are in the industry.
Net economy and e-business
The range of e-business is determined by the net economy. This refers to the commercial use of digital data networks for handling information, communication, and transaction processes via various platforms.
Since the late 90s, or even earlier, the development of digitalization not only led to a major structural change in society, but also in the economy. Since then, the focus has shifted to the information sector. The systematic use of technology to collect and utilize information laid the foundations of a so-called “information economy,” in which competitiveness is achieved through knowledge superiority.
This section of the economy, known as the “net economy,” now exists in parallel with the traditional, “real economy.”
Market participants in e-business
E-business can take place between a large number of market participants: between businesses and consumers, various private individuals, public administrations, and other organizations such as NGOs.
Generally speaking, these various market participants can be divided into three distinct categories:
- Business (B)
- Consumer/citizen (C)
- Administration (A)
All three categories can play the role of either buyer or service provider within the market, meaning there are nine possible combinations for e-business relationships. Within this context, B2C and B2B belong to e-commerce, while A2B (administration-to-business) and A2A (administration-to-administration) are a part of the so-called e-government sector (also a part of e-business).
Function of electronic business
The most important role of electronic business is “electronic value creation” – the generation of electronic added value. The forms of electronic added value are usually distinguished in the following way:
- Structuring value: an online offer achieves an overview of a large quantity of information
- Selection value: an online offer provides specific database information upon request
- Matching value: an online offer makes it possible to merge inquiries from supplier and buyers more efficiently
- Transaction value: an online offer makes a business more efficient
- Coordination value: an online offer allows different providers to better combine their services
- Communication value: an online offer improves communication between different consumers
Depending on which type of value a company decides to pursue, they can choose one or more value activities – for example the collection, structuring, pre-selection, summary, or distribution of information. A so-called “digital information product” can also be created, offering added values which the customer is prepared to pay for. This information product may be a website, blog comparison portal, e-book, or a software application.
The electronic value creation process involves the following steps:
- Collecting large quantities of information to identify data relevant to the product
- Processing the information and transforming it into a product
- Transferring the final information product to the customer
- Repeat this process whenever new information becomes available – information products are not static and must be kept up to date
Besides the generation of electronic added value, the various long-term goals of the e-business must be determined, such as how best to automate commercial processes, or establishing new business models (such as cutting out middlemen).
Examples of e-business
There are countless examples of different e-business activities, but here is a brief selection.
The e-procurement sector includes the following activities:
- Organize the implementation of a desktop purchasing system (DPS) that supports the whole procurement process, such as checking stock availability and handle the order and payment
- Constructing and operating an online marketplace for products and services
- Integrating various electronic supplier catalogs into your own enterprise resource planning (ERP) system to support procurement, warehouse management, order processing, production management, and logistics
The e-commerce sector includes the following activities:
- Designing and maintaining an internet presence and/or an online store including: products or services accessible from anywhere at all times, multiple payment options, automatic e-mail notifications on orders, and customer support (live chat, hotlines, or help centers)
- Developing and provisioning additional content, such as an informational blog or comparison portal
- Expanding online marketing and targeting advertising to customers, for example by using big data from cookies, purchase behavior, and customer data
It’s worth noting that new technologies like the internet of things will likely increase the importance of other e-businesses not mentioned here.