What is FIDO2?
Logging onto a website using your user name and password is no longer the best certification method for various reasons. On the one hand, entering personal user information is becoming increasingly cumbersome due to the ever-increasing number of services an average person uses. On the other hand, the security of log-in data is increasingly at risk due to cybercriminals becoming sneakier and more technologically advanced. Targeted brute force attacks or seemingly harmless email phishing attacks accumulate so users often don’t even notice that their own login data has already been tapped.
The FIDO2 security standard addresses this problem by enlisting the help of two-factor authentication that uses security keys (FIDO2 keys) and hardware tokens. Thanks to the integration of the W3C standard WebAuthn, this procedure not only allows encrypted and anonymous log-ins, but also completely password-free log-ins. But how exactly do FIDO2 tokens and keys work and what do you need so that you can use this login procedure for your own web activities?
What is FIDO2?
FIDO2 is the latest specification of the non-commercial FIDO Alliance (Fast Identity Online), which was created with the aim of developing open and license-free standards for secure, worldwide authentication on the World Wide Web. First came FIDO Universal Second Factor (FIDO U2F), then FIDO Universal Authentication Framework (FIDO UAF), meaning that FIDO2 is the third standard to emerge from the alliance’s work.
At its core, FIDO2 consists of the Client to Authenticator Protocol (CTAP) and the W3C standard WebAuthn, which together enable authentication where users identify themselves with cryptographic authenticators (such as biometrics or PINs) or external authenticators (such as FIDO keys, wearables or mobile devices) to a trusted WebAuthn remote peer (also known as a FIDO2 server) that typically belongs to a website or web app.
The FIDO Alliance was founded in 2012 by PayPal, Lenovo, Nok Nok Labs, Validity Sensors, Infineon, and Agnitio. A year later, Google, Yubico, and NXP joined the association. Over the past few years, there have been various collaborations in order to establish the standards, for example with Samsung and Microsoft.
Why do you need security specifications like FIDO2?
FIDO2 provides the option of using two-factor authentication, in which the usual username password login is supplemented by an encryption with FIDO2 keys as well as an additional FIDO2 token (hardware), or a completely password-free authentication.
What both variants have in common is that they eliminate the standard user login with user name and password, which isn’t considered the most secure, as well as simple two-factor authentications (email, mobile app, SMS): This prevents cyber criminals using typical attack patterns such as man-in-the-middle attacks and phishing from succeeding and taking over the user’s account. Even if the log-in data is compromised, the FIDO2 login will only work with the respective hardware token or private key, which is also bound to a dedicated hardware.
The fact that FIDO2 is an open standard makes it easier for software and hardware developers to implement the standard in their own products so they are able to offer users this very secure login method.
How does FIDO2 work?
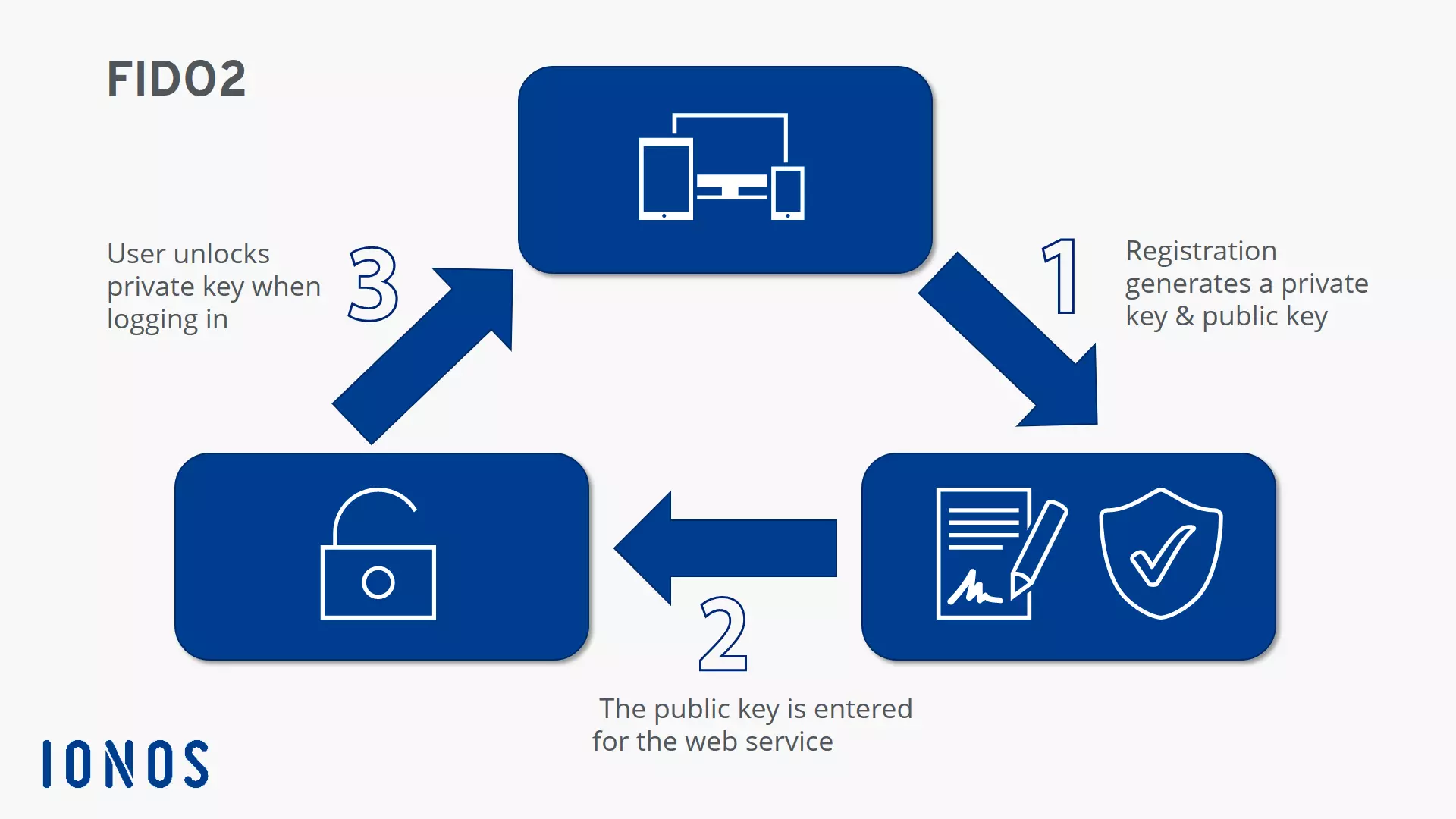
The main goal of FIDO Alliance is to increasingly eliminate passwords on the web. In order to achieve this, the secure communication path between the client (browser) and the respective web services is first set up or registered in order to be permanently available for later logins. In this process, FIDO2 keys are generated and verified, which provide the basic encryption for the logon procedure. The procedure is as follows:
- The user registers with an online service and generates a new key pair on the device used - consisting of a private key and a public FIDO2 key.
- While the private key is stored on the device and is only known on the client side, the public key is registered in the web service’s key database.
- Subsequent authentications are now only possible by verification with a private key, which must always be unlocked by a user action. There are various options such as entering a PIN, pressing a button, voice input, or inserting separate two-factor hardware (FIDO2 token). Some operating systems such as Windows 10 and Android can now also act as security tokens themselves.
The FIDO2 specification is designed to protect the user’s privacy. For this reason, no information is passed on that could give a hint about further web activities. Furthermore, biometric data, if this feature is used, never leaves the user device.
What are the requirements for using FIDO2 authentication?
The FIDO2 specification defines all components that are required for the modern authentication procedure.
First and foremost is the repeatedly mentioned W3C standard WebAuthn, which allows online services to enable FIDO authentication via a standard Web API (written in JavaScript) that is also implemented in various browsers and operating systems. Applications that already support the standard declared in March 2019 include Windows, Android, and iOS (version 13 or higher) as well as the following browsers: Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Apple Safari (version 13 or higher).
The second critical component is the Client to Authenticator Protocol (CTAP). This protocol enables the various FIDO2 tokens to interact with the browsers and also to act as authenticators. Both the browser used, and the desired hardware token must therefore be able to communicate via CTAP in order to use this security feature (including password-free login).
Advantages of FIDO2 over password authentication
This introduction has briefly explained why password-free or two-factor authenticated login procedures such as FIDO2 are the future. Compared to the traditional password log-in, they offer a much smaller attack surface for cyber criminals. With the right tools, it’s not difficult for criminals to work out passwords, while they would need the hardware security token to gain unauthorized access to a FIDO2-protected user account. In addition, you can use one FIDO2 token for different web services instead of creating and remembering different passwords.
The advantages of FIDO2 authentication at a glance:
| Higher security level | FIDO2 encrypts the log-in by default with a key pair (private and public) that can only be unlocked with the registered device. |
| Higher user comfort | In password-free mode, FIDO2 shows its strengths in terms of user convenience. Different passwords are just as much a thing of the past as entering the password itself - instead, a button click, voice input or plugging in hardware is enough. |
| Protection against phishing | If you use FIDO2, you don't have to worry about phishing even with the two-factor variant with password. Even if criminals obtain the password, they are denied access to the protected account. |
What are the disadvantages of FIDO2 authentication?
Although the FIDO2 process is advantageous in many respects, it also has its weak points: There are currently only a few web services that offer this form of authentication, and this is a basic prerequisite for their use. If FIDO2 is a possibility for you, make sure to plan for additional costs for purchasing external security tokens. Especially in companies where each employee needs their own security key, switching to FIDO2 can quickly become an expensive undertaking.
Finally, the standardized authentication method requires an additional step compared to an ordinary password log-in if it is implemented as a complementary component of a two-factor authentication. So, if you log on to one or more services several times a day, FIDO2 might not be one of the most efficient login techniques.