What is Microsoft Hyper-V and how does it work?
Hyper-V is a virtualization platform from Microsoft that allows multiple virtual machines to run on a physical server. The built-in Windows hypervisor makes it easy for users, as they are not dependent on external—and sometimes very complex—software.
What is Hyper-V?
To virtualize hardware, meaning to create a hardware environment that doesn’t physically exist in that form, you need an intermediary between the physical computer and the virtual machine. This interface is called a hypervisor. On the physical host system, multiple virtual guest systems can be mapped this way, sharing the host’s hardware. Microsoft has created its own hypervisor with Hyper-V, which is included directly in the professional versions of Windows 11, 10, or Windows 8. The software is also pre-installed in Windows Server.
Hyper-V gives Windows users the ability to start their own virtual machine. In this machine, a complete hardware infrastructure with memory, disk space, processing power, and other components can be virtualized. On this basis, a separate operating system can run, which doesn’t necessarily have to be Windows. It’s popular, for instance, to run an open-source distribution of Linux in a virtual machine.
Application areas of Hyper-V
Test environments
Virtualization technology can be used in various scenarios. However, Hyper-V is typically used in test environments. In this context, virtualization offers two main advantages:
-
Computer environments that are otherwise inaccessible can be represented. Instead of setting up a separate PC with Linux, you can relatively easily run the operating system in a virtual machine.
-
The virtual machine is also self-contained. So, for example, if you run software that causes a system crash, the physical device is not at risk. Only the virtual machine would need to be reset.
Private users can use Hyper-V, for example, if they want to run software that wouldn’t work with their current Windows version—either because the program requires an older version of the operating system or only supports Linux.
Especially for software developers, virtualization with Hyper-V is a great advantage: The program created can be tested under a variety of software and hardware conditions. Additionally, because of the self-contained virtual machines, there’s no worry about faulty code damaging your own system.
High availability and disaster recovery
Using Hyper-V can help minimize downtime and protect business-critical systems. A key technology is Hyper-V Replica, allowing virtual machines (VMs) to be asynchronously replicated to a second server. In case of a server failure, the replicated VM can be activated quickly to continue operations without major interruptions. Additionally, live migration enables the transfer of running VMs between hosts without shutting them down, easing maintenance and reducing downtime. For even higher availability, Hyper-V can be combined with failover clustering, allowing virtual machines to automatically move to another node in the cluster if a host fails.
Cloud and hybrid cloud
Hyper-V also plays a central role in virtualization within cloud and hybrid cloud environments, especially in connection with Microsoft Azure. Companies use Hyper-V to efficiently manage on-premises data centers while flexibly incorporating cloud resources. Through integration with Azure Virtual Machines and Azure Local, IT infrastructures can be operated and scaled both on-premises and in the cloud. Thanks to the previously mentioned Hyper-V Live Migration, companies can move workloads as needed. This hybrid cloud functionality offers flexibility, reduces hardware costs, and improves the scalability of IT resources.
Architecture of Microsoft Hyper-V
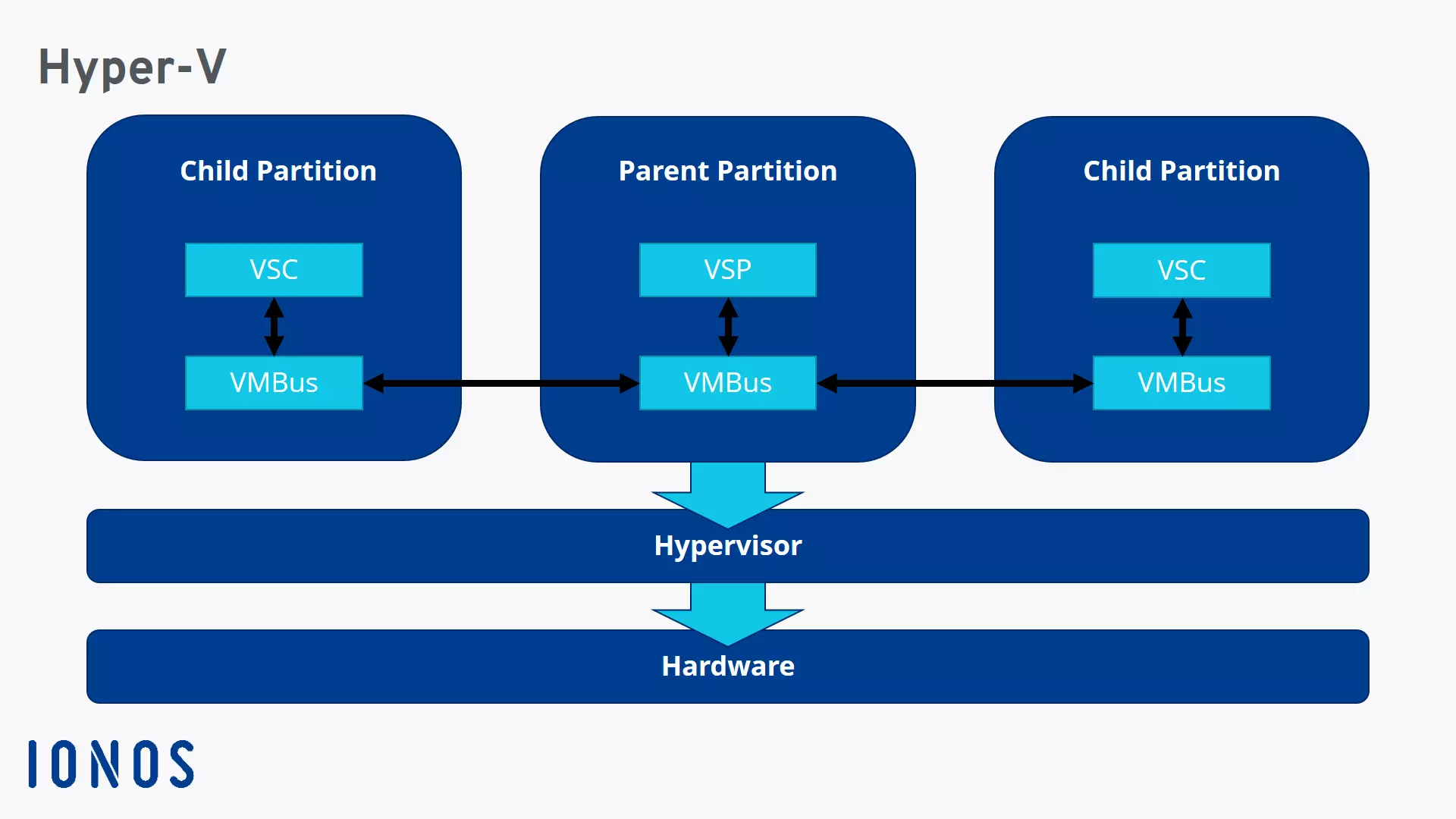
With Hyper-V, one or more virtual machines can be hosted on x64 versions of Windows, each containing a fully configured operating system. These guest systems are treated as partitions. This term is familiar from disk partitioning, and virtualization via Hyper-V works similarly. Each virtual machine is an isolated unit alongside the parent partition, which is the actual operating system.
The individual partitions or guest systems are orchestrated by the hypervisor. Through an interface (the Hypercall API) in the host system, the subordinate partitions can be created and managed. However, isolation always remains intact. Guest systems are allocated virtual hardware resources but can never access the host’s physical hardware. To request hardware resources, subordinate partitions use the VMBus. This is a channel that enables communication between the partitions. Guest systems can request resources from the host and theoretically also have the capability to communicate with one another.
Services run on the partitions that process the requests and responses running over the VMBus. The host system runs the Virtualization Service Provider (VSP), and the subordinate partitions run the Virtualization Service Clients (VSC).
Differences between Hyper-V and other virtualization techniques
Unlike all other virtualization solution providers, Hyper-V has the advantage of being closely integrated with Windows. Users of the Microsoft operating system for PCs or servers can benefit from this good integration. Hyper-V is also a Type 1 hypervisor, which only a few other solutions offer. This means Hyper-V runs directly on the system’s hardware. When comparing Type 1 and Type 2 hypervisors, the central difference is that the latter always has to go through the host’s operating system to provide resources.
Advantages
For Windows users, a very clear advantage is the close integration with the operating system. This can also have budgetary benefits, as Hyper-V is often included for free with Windows. In terms of functionality, Hyper-V competes well with its rivals. Regarding performance, users don’t have to compromise with Hyper-V (as long as they work only with Windows as the guest system). Since management is relatively simple, beginners can also benefit from virtualization.
Disadvantages
While Hyper-V works very well with Windows, the software reaches its limits with other operating systems. For one, Hyper-V is not designed to run on other systems, and the potential guest systems are very limited. Outside of Windows, only a few selected Linux distributions can run in a virtual machine. For example, those wanting to use macOS as a guest system must choose a competing product. It’s also been noted that when running multiple Linux guest systems, significant performance losses should be expected.
For those who primarily operate within the Windows environment, Hyper-V is a good alternative to other virtualization solutions. Since the software is often already installed under Windows (or can be added for free), Hyper-V is also well-suited for smaller projects. However, the software clearly shows weaknesses when dealing with other operating systems.
Alternatives to Hyper-V
Those looking for alternatives to Hyper-V have several powerful virtualization solutions to choose from.
- VMware: One of the best-known is VMware vSphere, widely used in corporate environments due to its stability and high scalability. For smaller businesses, VMware Workstation and VMware Fusion are suitable, user-friendly, and compatible with many operating systems.
- VirtualBox: VirtualBox is a free open-source software from Oracle, particularly suitable for testing purposes and smaller virtualization projects, and available for both Windows and macOS.
- Proxmox: Proxmox VE is an open-source alternative for server virtualization. Both KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) and LXC containers are supported.
- KVM / QEMU: QEMU is a virtualization solution integrated into Linux. It provides a flexible and high-performance alternative, though it often requires more manual configuration.
- Parallels Desktop: For macOS users, Parallels Desktop is one of the best solutions as it is specifically optimized for Apple devices.
- Cost-effective vCPUs and powerful dedicated cores
- Flexibility with no minimum contract
- 24/7 expert support included

