SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol)
The SSH File Transfer Protocol ensures that data is transferred securely between two communicating parties, which has become essential for many work processes in companies. For example, field service agents send their work results to the company headquarters, the server architecture of a company network is kept up to date and secure via remote maintenance and repair instructions are accessed online by the on-site repair technician. To do this, data must be transferred bidirectionally over an Internet connection to and from the company server. Files for websites are also sent in this way to the corresponding web spaces. The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) has been used to perform this data transfer since 1971.
Data management via FTP is similar to working in Windows Explorer, Mac Finder or Linux Nautilus. The difference is that data is transferred to and from the remote servers. The transfer tunnel to and from the user (FTP client) and server (FTP server) always presents a potential point of attack for data theft and tampering or the introduction of malware into the user’s system. Not to mention, the lower the security standard is, the greater the threat, and FTP is very low. Using FTP, the username and access password are sent in plain text (i.e., unencrypted). Potential attackers can thus intercept the login information and gain unauthorized access to the FTP client and server - with obvious consequences.
To avoid these potential attacks, SFTP was developed as an alternative with significantly improved security.
What is SSH File Transfer Protocol?
One of the measures taken to improve the security of FTP data transfer was the development of the SSH (Secure Shell) File Transfer Protocol. This protocol ensures secure authentication between communicating parties. As soon as a client starts the login process, the server verifies the client’s identity via and with SSH. The two-way authentication is performed using certificates and the public and private key procedure. Access is only authorized if the SFTP client’s key fits the SFTP server’s “door lock.” The server verifies whether the client has “unlocked” the data tunnel with a matching key.
This key consists of a randomly generated sequence of letters, numbers, and special characters with a fixed number of bits. This is called a cryptographic protocol. It enables communication to be encrypted even when using an unsecured Internet connection.
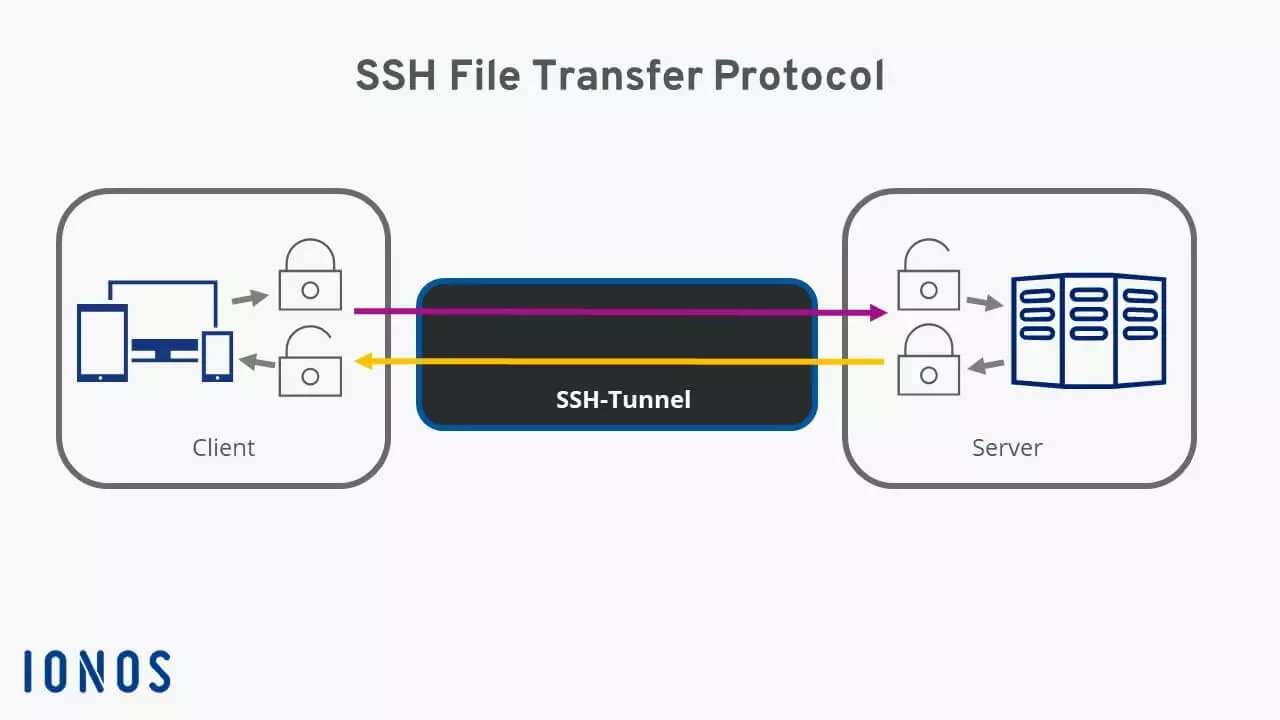
SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP): This protocol ensures encrypted data transfer to and from client and server systems over a single connection. Both the data of the established connection and the transferred data are encrypted with keys using the SSH protocol.
How does SFTP work?
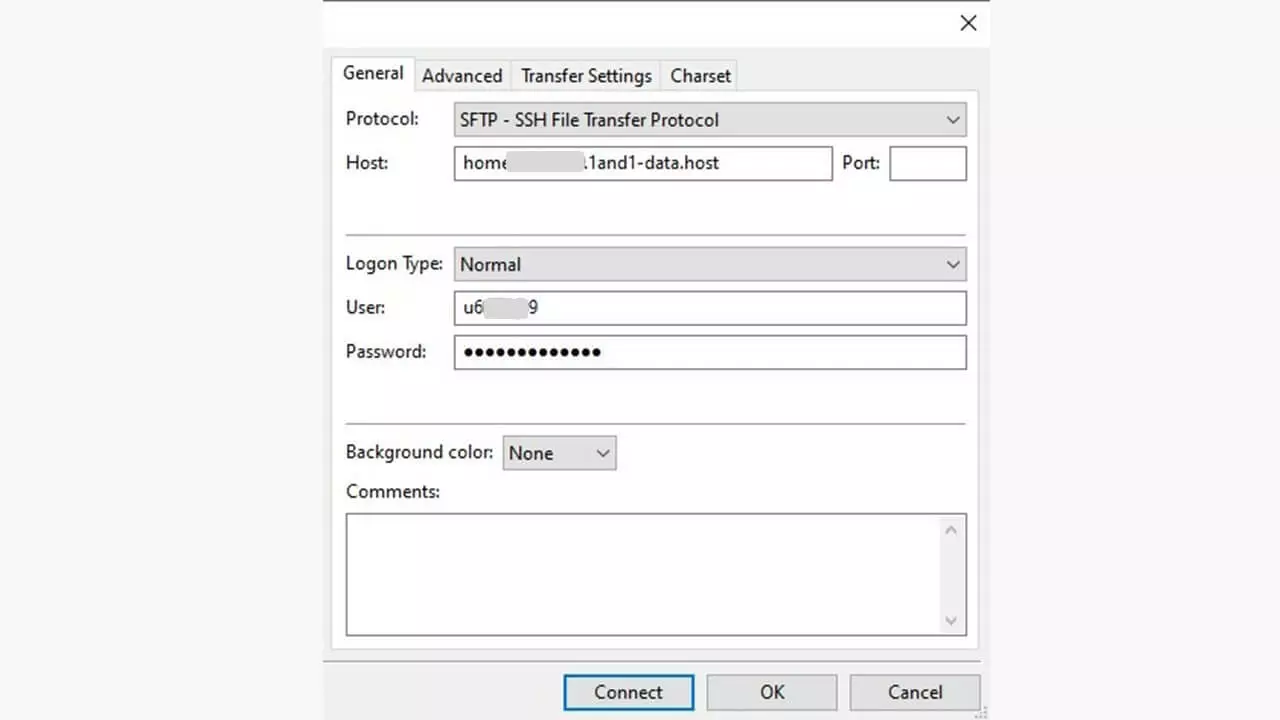
SSH access on the host’s server is required for a functioning connection using the SSH File Transfer Protocol. This provides the access data for the SFTP user: the server address, username, and password. This data is entered into the (S)FTP program used by the client. When the connection is first established, the key for verification is displayed and stored in the FTP program for future use. The client uses this key to authenticate itself to the server every time a connection is established. If a website or attacker tries to “authenticate” itself during communication using an incorrect key or no key at all, the connection will be immediately terminated.
There is a bidirectional SSH tunnel between the client and the server through which authentication and data transfer are conducted. This tunnel is fully encrypted so that no attacker can access any data. The data thus arrives at the recipient without having been tampered. If an attacker still attempts to modify the data while it is being transferred, SSH will detect the tampering and immediately terminate the connection.
Data transfer using the SSH File Transfer Protocol thus protects against the following:
- Modifications made to the IP address of a data packet – i.e., IP spoofing
- Redirection of the originally addressed computer name to the attacker’s IP address (i.e. DNS spoofing)
- Interception by an attacker of access data in plain text
- Tampering of the transferred data by an attacker
SFTP does not protect users from being careless with user data and keys!
Using the SSH File Transfer Protocol
In the (S)FTP program, the protocol is selected in the dialog box where the login information is entered. In the client application FileZilla shown below, this is the server manager. Usually, you will not need to select a port as the port is automatically set to 22 when SFTP is selected.
We have put together an overview of recommended (S)FTP programs in our article “10 FTP programs or FTP clients for Windows & Mac”.
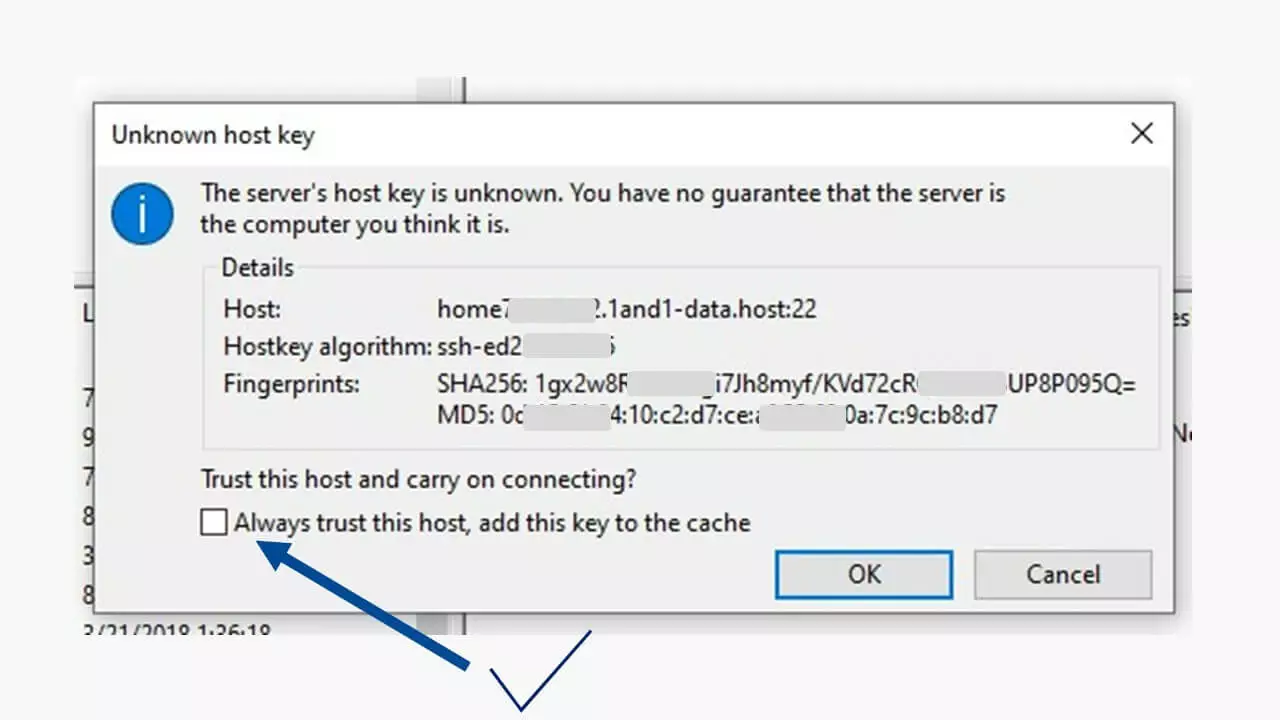
The first time you try to connect using the SSH File Transfer Protocol, the SFTP client will receive a message that shows the SSH security standard.
You should check once again that the server address is correct. When you look at the entry for the server, you will see that the correct port, port 22, is being used since the entry displays “home….-data.host:22”. By selecting the checkbox next to “Always trust this host, add this key to the cache” and then clicking “OK,” the connection data will be saved and the encrypted connection established.
This data will not be requested again the next time a connection is established since the SFTP client identifies itself to the SFTP server with the unique key. This digital signature encrypts all data transfers, including the login data for establishing the connection. The status window in the FTP program will display any notifications about the progress of the download or upload.
For data storage or transfer, IONOS offers SFTP servers for rent which include personal accounts, backups and app management.
What is the difference between SFTP and FTP?
The main difference is that authentication and any data traffic between the client and server are encrypted in SFTP data transfers. Even if an attacker succeeds in intercepting the data, they will not be able to use it. If the SSH File Transfer Protocol detects any login information that has been tampered with or any attempted attacks, it will immediately terminate the connection. The following is a brief overview of the differences between FTP and SFTP:
| FTP | SFTP | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of channels used | 2 separate ones | 1 |
| Encryption standard | None | SSH2 |
| Encrypts authentication | ||
| Encrypts data transfer | ||
| Vulnerable to attack (interceptions, attacks) |
The technical security of this cryptographic data transfer should be improved upon both on the client’s side and server’s side with additional security features. This includes decisions regarding things such as physical location, the physical security of the SFTP server, and secure data storage for clients accessing the server. Generally, if you are careless with data, you will face the consequences sooner or later.