What is a Broadcast?
Packets in IT networks can be sent to all participants via broadcast without the recipient addresses being known. For this purpose, each network has a reserved broadcast address to which a limited or directed broadcast can be sent.
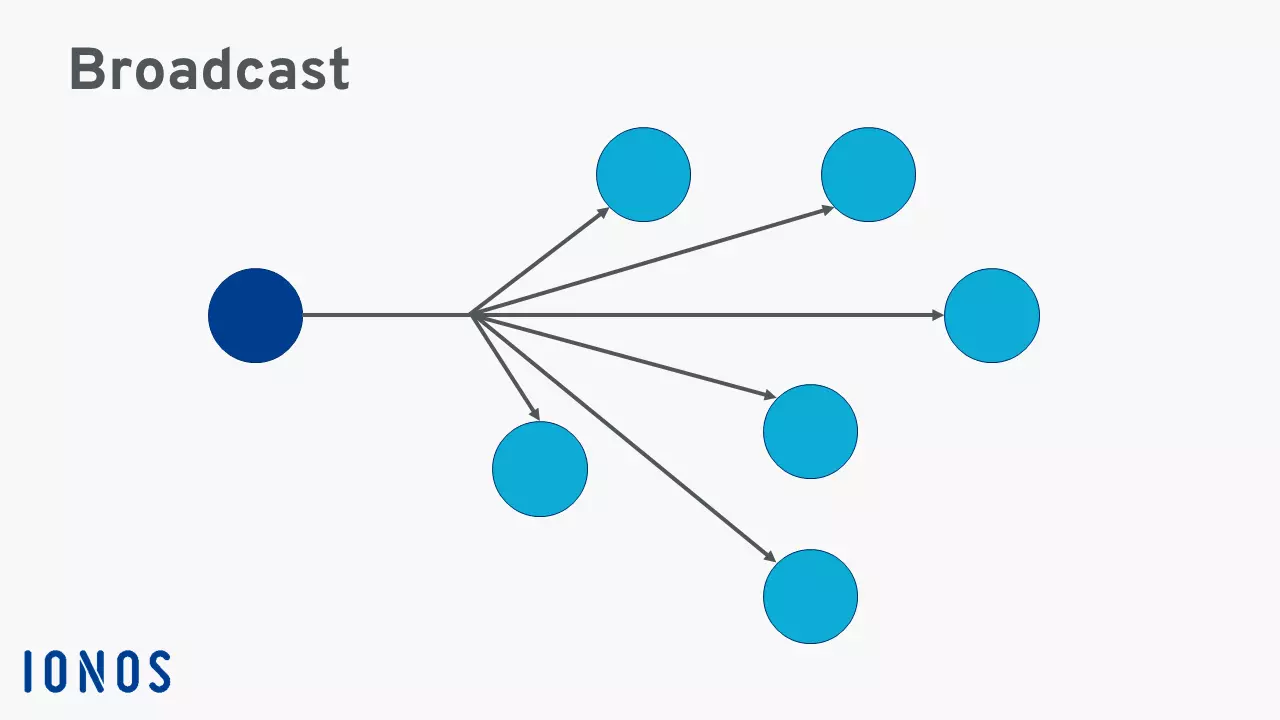
Broadcast – what is it?
A broadcast in a computer network is a message that is transmitted to all participants in a network and does not require a response. A computer in a network sends a data packet simultaneously to all other participants in the network. The sender does not have to specify any recipient addresses — this distinguishes the broadcast method from unicast, in which only a single, known recipient is addressed.
The general advantage of a broadcast is that information can be widely distributed and does not have to be transmitted multiple times. To implement the procedure, a special address is required that replaces the respective recipient addresses. This broadcast IP is mainly used when the addresses of the individual network participants are unknown.
A broadcast is a multipoint connection in a computer network. In this case, a data packet is transmitted from one point to all participants in a message network. This is done using the broadcast address.
Basics of broadcast technology
Addressing is used to transfer data for communication in a network via the Internet protocol from one system to another. The IP address enables the unique forwarding and delivery of data packets from the source to the destination. Like a telephone number, this address can be subdivided into a prefix and a call number - except that IP addresses are named network and host parts. This subdivision is done with the help of the netmask, which is placed over the IP address like a template. A netmask is just as long as an IPv4 address. It describes which bit positions within the IP address function as the network or host part.
IP address
An IP address is a numerical designation. Each device connected to a computer network based on Internet technology is assigned an IP address. This IP address uses the Internet protocol for communication. An IP address performs two main tasks: Identifying host or network interfaces and addressing location.
The Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) defines an IP address as a 32-bit number. Due to growing demand and the exhaustion of available IPv4 addresses, a new version of the protocol with 128 bits for the IP address was developed in 1995 with IPv6. In December 1998, this was standardized. A final definition of the protocol was published in July 2017. IPv6 deployment has been underway since the mid-2000s.
Ethernet
For wired data networks, software and hardware are interconnected using Ethernet technology. This technology enables data exchange between locally connected subscribers. The Ethernet network is the wired network’s most widespread technology, especially in company networks and home networks. Furthermore, the Ethernet often forms the basis for intranets.
MAC address (Media Access Control)
The MAC address is the address of a network device. It is usually written as a hexadecimal number, such as 08-00-20-ae-fd-7e or 08:00:20:ae:fd:7e (or also: 080020aefd7e).
Broadcast address
The broadcast address sends the data and information to all devices in a network. The network components are responsible for receiving and processing the data. The task of the broadcast IP address is to connect all network devices with each other. We provide more information on this in our detailed article on the broadcast address.
How does a broadcast work?
A connection setup via broadcast is initiated by the sender. The sender sends their address, which the recipients can use to contact them. A broadcast therefore functions similarly to a mailing list, in which the recipients are not visible — and the sender does not need to know the addresses of the network participants. Only when the participants contact the sender do they reveal their own addresses. The network participants can open the data packets and then interpret the information, execute instructions, or reject them.
A distinction is also made between limited and directed broadcasts:
Limited broadcast
With the limited broadcast, an IP address is specified as the destination. This IP address is always 255.255.255.255. Technically, this broadcast targets all existing IP addresses. In fact, however, the specified IP is understood to be the address for the broadcast in this network. This destination is always in the user’s own network and can therefore be implemented with the help of an Ethernet broadcast. A router does not forward packets like this.
Directed broadcast
With a directed broadcast, all recipients within the target network are always addressed. In this case, a combination of the number of the destination network and setting all host bits to 1 results in the broadcast address. If the destination is not in its own (sub)network, a router will forward the data packet.
Host bits are the part of an IP address that identifies a particular host in a subnet. The subnet mask determines which portion of the address is used for network bits and which is used for host bits. For example, the IPv4 address 192.168.0.64/26 has a 6-bit host portion because 26 of 32 bits are reserved for the network portion.