WordPress
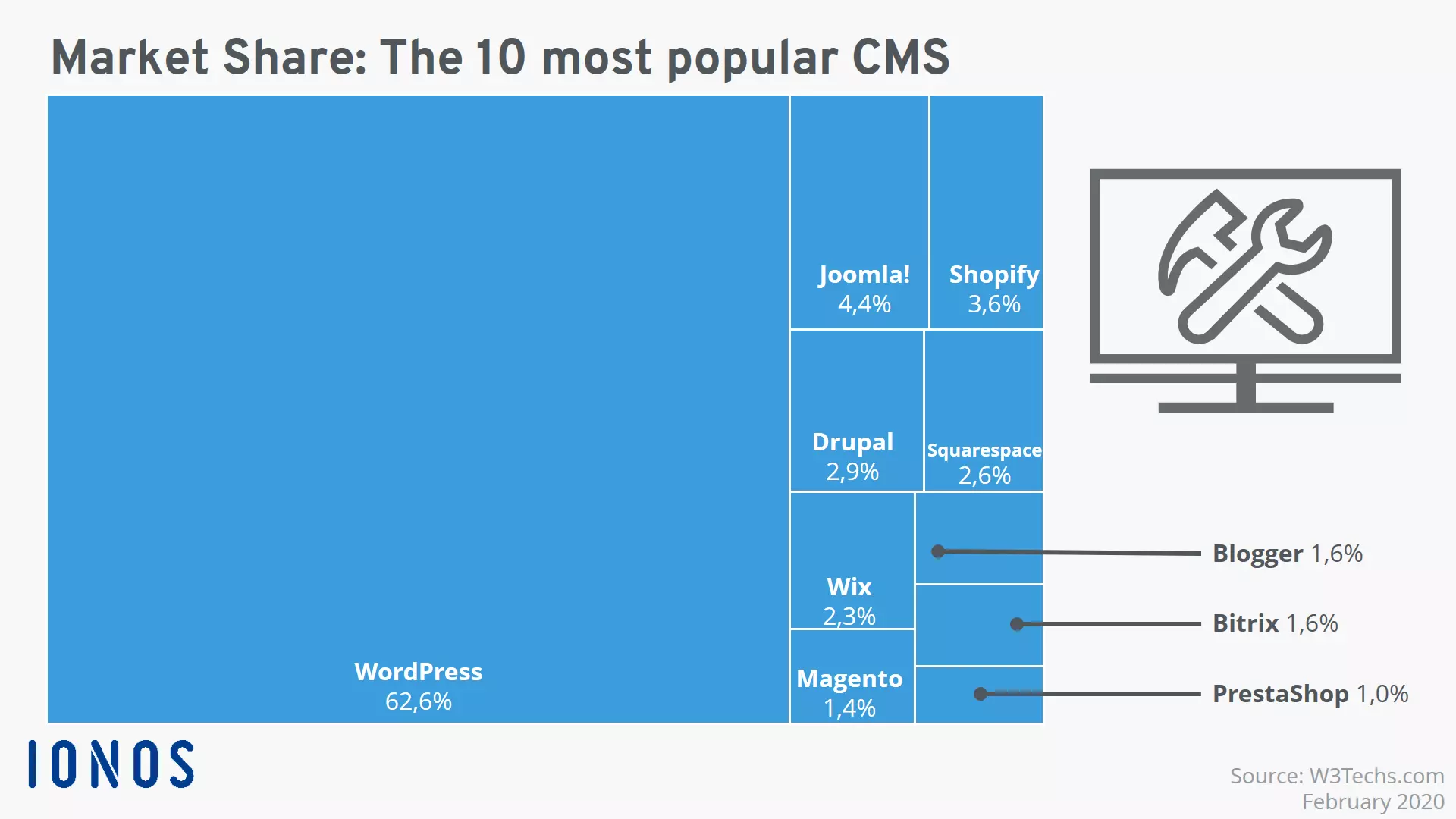
For a long time now, the free CMS WordPress has been the premier blogging software. It’s simple really: those who run a blog, use WordPress. A comparison of the most popular CMSs of WordPress functions compared to other large content management systems like TYPO3, Joomla!, or Drupal, however, shows that WordPress has significantly expanded its spectrum as a CMS. While it is still geared around the creation and management of a weblog, the customization features offered on WordPress mean it can be used for comprehensive business pages, news portals, and web stores.
- Create & customize your site with AI tools made for everyone
- 3x faster: SSD, caching & more
- Daily security scans, DDoS protection & 99.98% uptime
What is WordPress?
In 2003, Matthew Mullenweg and Mike Little developed the blog software WordPress on the basis of the weblog system b2/cafelog. Later, b2 creator Michel Valdrighi joined the developers group, so that WordPress could be declared the official successor of b2 shortly after the release of the first stable version on January 3, 2004. In the following years the team worked meticulously on the further development of the GPL-licensed, free software, whereby the range of functions was continuously extended. The pure blogging application was gradually transformed into a full-fledged content management system, which won WordPress the Open Source CMS Award in the category "Overall Best Open Source CMS" in 2009.
WordPress has a modular structure, whereby the individual modules are written in the script language PHP. A distinction has to be made between the core modules, which form the starting framework for the installation of the software, and additional modules (plug-ins, themes), which extend the CMS with new functions or layouts. WordPress provides a relational database management system for data processing, whereby the developers recommend the use of MySQL or MariaDB. Further information on the topic "What is WordPress?" can be found in our article on the most important WordPress terms.
Since 2005 the company Automattic, which Matt Mullenberg founded together with some other developers, has been coordinating the further development of WordPress. The company also offers various supplementary services for the CMS. With wordpress.com a hosting service for WordPress projects is part of the portfolio, which can be used either free of charge (basic version) or with a paid subscription (versions with additional features).
Who is WordPress as a CMS suitable for?
Over the years, WordPress has developed into a true all-rounder CMS, which is also recommended for beginners despite its significantly increased complexity. If you want to create a web application with WordPress, you do not need extensive knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Functional elements as well as design and content can be implemented and adapted via the intuitive interface of the WordPress backend without having to write your own code. The CMS software generates this code automatically in the background.
Thanks to the integrated user management, you can easily work together on projects: Individually definable user roles control which user has which rights in the backend and, for example, has free editing options or may only edit posts. WordPress even provides six pre-defined standard user roles to get you started:
- Super Administrator: User has all rights and can make any changes (multisite projects such as multilingual websites)
- Administrator: User owns all rights and can make any changes (standalone WordPress sites)
- Editor: User can manage all contents of any WordPress page
- Author: Users can create, edit, delete and publish their own posts and upload files.
- Contributor: User can create, edit and delete posts
- Subscriber: Registered users who can comment on posts and view their profile in the backend.
Application scenarios: What is possible with WordPress?
Although WordPress was originally designed for bloggers, it is now also suitable for various other types of websites. While the creation of a weblog is undoubtedly the most common field of application for open source software, many other projects are now also realized with WordPress. For example, companies and the self-employed have been using the CMS for several years now to implement a professional, modern company website - the same applies to clubs that want to keep their members up to date via their website. WordPress also shows its strengths when it comes to the design of typical content such as imprint, terms and conditions, or the contact page.
Thanks to relevant extensions, the content management system is also suitable for creating community websites with forums and social media as well as for operating your own online stores. These features help bloggers, but they are also useful for company websites, news portals, online magazines, web stores, and community platforms. Well-known sites realized with WordPress include the New York Times Company, fashion magazine Vogue, rock band the Rolling Stones, Sony Music, and the official website of Sweden.
WordPress is also interesting for various web projects because the CMS provides first-class support in search engine optimization. You can find out exactly how this support works and which plug-ins play an important role in it in the WordPress SEO tips article.
WordPress features overview
The WordPress focus is on being easy to use. Users don’t need experience with PHP or HTML – this CMS offers useful options to help anybody create and edit their online presence. Some of the basic features include:
- A WYSIWYG editor for writing articles that is quite similar to a text-writing programs like Microsoft Word.
- The WordPress Media Library for embedding images, videos, and audio files easily.
- DFour different roles (administrator, editor, author, contributor, etc.) for creating and editing content.
- The option for site visitors to create their own account in order to get access rights to certain parts of the site (e.g. only registered users are allowed to comment on posts).
- A tool allowing website users to subscribe to posts on their newsfeeds.
- A responsive design for both the front end (site visitors) and back end (page editors) of the WordPress site.
While the listed features are already available in the standard installation of the content management system, WordPress can be extended as mentioned. A distinction has to be made between plug-ins and themes. While the former add additional functional elements to the CMS, the latter change the layout and the appearance of the front or back end of your WordPress project.
WordPress: CMS with enormous plug-in bandwidth
By comparison with other CMSs, WordPress offers a huge number of add-ons, mostly thanks to its substantial community. There are already more than 40,000 extensions, with figures rising. The following is a list of some of the best and most coveted plugins, which can be downloaded for free from the official WordPress site:
-
Jetpack: this helpful extension gives access to over 30 different tools for optimizing a WordPress page and simplifying admin tasks. Among other features, Jetpack displays visitor statistics and gives tips for increasing site traffic.
-
Wordfence Security: even the standard version of WordPress is seen as a very secure CMS, but this add-on further protects sites from hacking and malware.
-
WP-DB-Backup: this tool creates a quick and easy backup of your database.
-
NextGen Gallery: this extension allows you to manage photos, create galleries, and add digital watermarks to photos and graphics.
-
WooCommerce: this online trading plugin offers users a wide range of ways to implement a web shop with WordPress.
Further information about plug-ins and a list of the best free and paid representatives can be found in our article about the best WordPress plug-ins.
WordPress SEO plugins
Even the free WordPress format is quite well-equipped when it comes to search engine optimization (SEO). But the following extensions improve the ranking of a WordPress site further still:
- Yoast SEO: this complete SEO package has been popular for years. It features tools for page analysis, optimizing meta and link elements, social media integration, and much more.
- All-in-One SEO Pack: another plugin that combines many SEO features, this extension can also be combined with the aforementioned WooCommerce add-on.
- Google XML Sitemaps: this tool creates sitemaps to your website that search engines can index more efficiently.
- W3 Total Cache: this very complex plugin optimizes site performance.
- Broken Link Checker: this extension analyzes your website for broken links and suggests appropriate action.
New themes for WordPress sites
In addition to the numerous plugins available, WordPress has a large number of WordPress themes on offer. Themes – also known as skins or templates – determine the design of a website. Choosing a theme also helps highlight one particular website function. This means you can adjust your WordPress site to specific requirements. If you want to make your website accessible, then selecting the right theme is crucial.
New themes (some free and some subject to a cost) can be downloaded from the official WordPress website. Further design ideas can be found on GitHub. The largest collection of WordPress themes is available from Themeforest, with over 6,000 different themes at a range of different prices.
Unfortunately, the vast collection of themes and plugins poses certain security risks. Not every extension is produced by professional developers. In some instances, they are poorly maintained and missing necessary updates. Since this can quickly lead to security gaps, it is important to update your extensions regularly to protect your system.
Creating your own website with WordPress: How does the installation work?
WordPress makes it as easy as possible for users in many ways. This starts with the installation, which only takes a few minutes. Before that, however, it is necessary to have all the prerequisites, whereby the requirements for software and hardware are very low: First of all, you need the web space on which you will host and manage the CMS and the content of your web project. Here you should provide enough memory and computing resources (RAM, CPU) to ensure the smooth live operation of the website. If the website is to be available online, you also need a suitable domain address, which you link to your WordPress project during installation or setup.
- Free Wildcard SSL for safer data transfers
- Free private registration for more privacy
- Free 2 GB email account
Other mandatory software besides the WordPress CMS, which you can download directly from the official website, are current versions of PHP and MySQL (or MariaDB) as well as a web server that supports them. According to the development team, Apache and NGINX are the most robust and powerful servers for WordPress operation, which is why you should definitely prefer one of the two solutions. Once you have the web server of your choice up and running, you can install WordPress on your web space via FTP (Local installation is of course also possible). Then set up the CMS step-by-step according to your ideas and needs.
WordPress: Hosting on your own or managed hosting?
As with any website, you also need to decide where to host it. Hosting on your own server or locally on your own computer (for test purposes) has already been mentioned briefly. In this case you have maximum control over your data, but you also have to take care of the setup and maintenance of all hardware and software yourself. Hosting on your own is therefore recommended for more experienced users who are familiar with server operation and have the necessary resources.
The alternative to self-arranged hosting is to rent a hosting environment from a provider. If you choose this option, you do not have to worry about setting up or maintaining the server. In addition, most hosting providers offer ready-to-use installation packages for the most important web applications, which can be used to install CMS such as WordPress including web server and database with just a few clicks. You can also have managed hosting with IONOS - including bonus services such as domain address, e-mail inboxes, SSL certificate, and 24-hour support.
The WordPress developer Automattic also offers its own managed hosting service. To use this service, register on wordpress.com. During the registration process, you have the choice between:
- free use of the software (very limited functionality, little web space; your site is a subdomain of WordPress, e.g. website-xyz.wordpress.com)
- and several fee-based variants (with an own domain, many additional functions and a higher storage capacity).
Summary: Strengths and weaknesses of WordPress
The variety of plug-ins is one of WordPress’ greatest strengths - but due to the already mentioned security risks due to outdated or faulty extensions, it is not always advantageous. Further shortcomings include the limited possibilities of user and rights distribution and that it’s quite complicated to implement a multilingual website. The missing functions can be added with extensions, but when implementing very complex websites, you usually have to change many plug-in settings - one of the main disadvantages of WordPress.
Overall, however, the strengths outweigh the disadvantages – there’s obviously a reason that WordPress holds its leading position compared to the competition: Internationally, it is by far the most widely used CMS. If you use WordPress as your CMS, you will benefit from its popularity since the large community not only provides an immense supply of plug-ins and themes, but also quickly helps you with questions and difficulties. You also benefit from regular system updates. And if you ever need professional help, you can take advantage of the support of various external service providers who specialize in WordPress support.
Another big advantage of the CMS market leader is its easy operation - especially for beginners. With the WYSIWYG editor, drag-and-drop operation, a practical media library, and other useful functions, you can achieve significant web design results even without HTML knowledge.
| Advantages of WordPress | Disadvantages of WordPress |
| Open source | Security risks due to plug-ins |
| Free | Popular target for cyber criminals |
| First-class SEO- features | Limited possibilities for allocation of user rights |
| Easy, intuitive operation | Regular updates for WordPress as well as plug-ins necessary |
| Large community | Complicated to implement multilingual sites |
| Versatile | |
| High performance thanks to minimalist program code | |
| Highly expandable |