Disabling cookies: how to turn off cookies in your browser
The internet’s anonymity is aptly illustrated in the classic cartoon of two dogs seated at a computer, one saying to the other, “On the internet, nobody knows you’re a dog.” Of course, in actuality, everyone who uses the internet leaves a virtual footprint with every click, even if many users aren’t aware of this. For example, cookies are commonly used to store browsing history and record user preferences, making them among the most important tools for data collection on the internet. However, the interests of website visitors aren’t always behind the use of cookies. Since this cached data can often be used and sold for political and business purposes, an increasing number of users choose to disable cookies in their browsers.
In accordance with the new EU directive on the use of cookies an operator must explicitly inform visitors about the use of cookies on a website with the exception of cookies that are necessary from a purely technical point of view.
Turning off cookies: the subtle difference between session and tracking cookies
Cookies are tiny text files that store information about a user’s behavior when visiting a website. When opened, a site generates a cookie which is placed in the user’s computer by the browser. This will be available for future repeat visits to the site, allowing the server to recognize the user so that settings can be stored permanently as well as for the placement of personalized advertising.
Saving of data is usually done anonymously.
There are a number of application possibilities for cookies, and the text files also differ from one another. Some cookies are important for a site’s user friendliness and others serve primarily commercial purposes. So, before you start deleting cookies, it helps to know what function they perform to help you decide which are harmless and which are better to block.
Session Cookies, etc. – useful cookies for an optimal user experience
So-called persistent cookies are harmless and provide a better user experience. If you change your Yahoo! mail interface color, the browser stores this information on your computer with the help of a cookie. The browser then later remembers your chosen setting and automatically displays the Yahoo page in the selected color, thanks to the cookie.
Session cookies are similarly harmless. These store data such as usernames and passwords (in encrypted form) for a shorter time. In online banking, for example, the browser remembers the access data for the duration of the user session but deletes the information from the cookie as soon as the session has ended.
A virtual shopping cart is another classic example of a session cookie. You can load any number of pages on a shopping site and switch from tab to tab – and yet at the end of the session, all your selected products are stored in your shopping cart. However, if you close the website, in most cases the data will be deleted from the shopping cart.
Tracking cookies – controversial data collectors
If a cookie is stored on the user’s hard drive to be able to recognize and track it later, this is called cookie tracking. While the user isn’t in any way limited by this kind of data collection – it runs entirely in the background – you can’t be completely sure of what happens to this data. While the use of tracking cookies as instruments of affiliate marketing and web analysis is essentially harmless, there are certainly scenarios in which user information is used beyond its normal purpose or even passed on to third parties. Furthermore, an explicit danger exists from cookies planted by cybercriminals or when distributed by dubious websites whose aim is to collect as much data as possible.
In summary, tracking cookies can be roughly divided into the following three groups:
1. Affiliate
Cookies are important for affiliate marketing, since the affiliate marketer receives a commission for any purchases by users through the referral. Without tracking or tracking cookies, there would be no way of noting the source of the referral, and the affiliate misses out on their commission. The cookie duration – the period in which the cookie is valid – determines how long an affiliate marketer has a recognized role in any transactions. The same applies to identification of the user. Cookie tracking is not only used for affiliate marketing, but also to create user profiles.
2. User profile creation
Companies use cookies to create user profiles in which the user’s browsing behavior, interests, and preferences are tracked and stored. Such cookies work in tandem with other cookies, allowing them to collect even more user behavior data across multiple pages. This data is used to analyze more complex patterns in user behavior and to present targeted personalized ads to the user.
Although cookies are extremely valuable for businesses, advertising agencies, and above all for online shops, there are numerous privacy concerns about cookie tracking.
3. Malicious cookies
Malicious websites can store cookies on your computer and record your internet activity. These text files can also pass any captured data on to third parties, which is what makes them so dangerous. Like all other “harmless” cookies, these cookies are stored on your PC when you visit certain websites. Privacy advocates warn that tracking cookies compromise users’ privacy while the advertising industry makes the argument that all data is collected anonymously, meaning it can’t be identified with a particular individual.
You can protect yourself from these tracking cookies by disabling cookies.
Customise cookie settings in your browser
Using the default settings without deleting cookies in Google Chrome or other browsers such as Firefox, Internet Explorer, or Safari makes for an uncomplicated daily network experience, but tracking via cookies is taking place.
Users can change their cookie settings or delete existing cookies (individually or completely). The following options are available in most browsers:
- Block cookies
- Block third-party cookies (e.g. banner ads)
- Obtain permission for each cookie (usually three options: “allow permanently,” “allow for a session,” or “decline”)
- Delete all cookies when closing the browser
Some browsers also give the user the option to view the data stored in the cookie or to delete individual cookies.
How many files individual cookies are stored in varies from browser to browser. In some browsers, each cookie has its own file, while for others such as Firefox, all cookies are stored in a single file.
Each set up has advantages and disadvantages: regular requests to a browser regarding whether cookies are allowed can quickly get annoying. For this browser request option, you should be familiar with cookies and the websites that you want to visit in order to know when to allow cookies and when not to. If you disable cookies altogether, some websites will display error messages or be of limited usability, since some pages only operate on an error-free basis when cookies are enabled. Nonetheless, with cookies disabled, you can be certain that your own data is secure.
How do I block all cookies or partially block cookies in different browsers?
Partially or completely blocking cookies is slightly different in each browser. To follow, we’ll show you how step by step.
Disabling cookies in Chrome
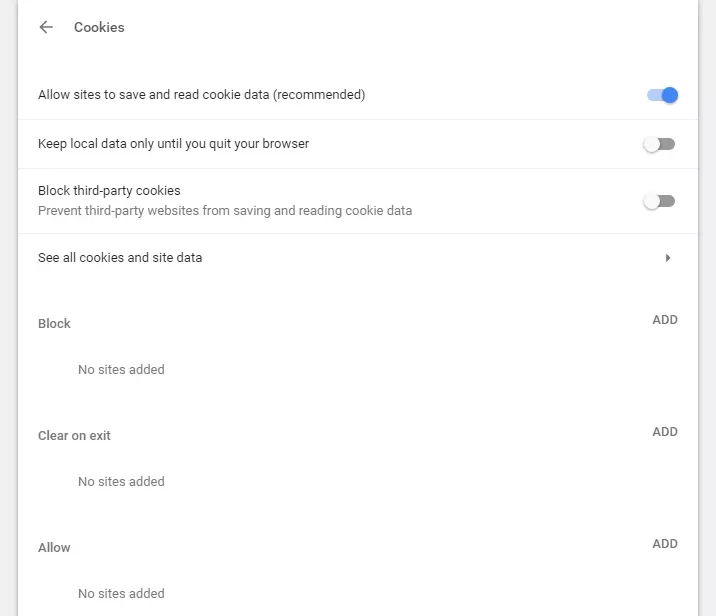
Step 5: “Cookies” takes you to the relevant settings.
Step 6: Move the slider next to “Block third-party cookies” to the right to block all third-party cookies. You can also turn on the “Keep local data only until you quit your browser” to clear all data at the end of a session.
Step-by-step instructions for how to disable cookies in Google Chrome:
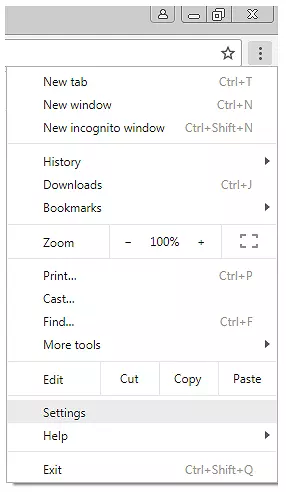
Step 1: Click the symbol with the three dots in the upper right corner.
Step 2: Then choose “More tools” and “Clear browsing data.”
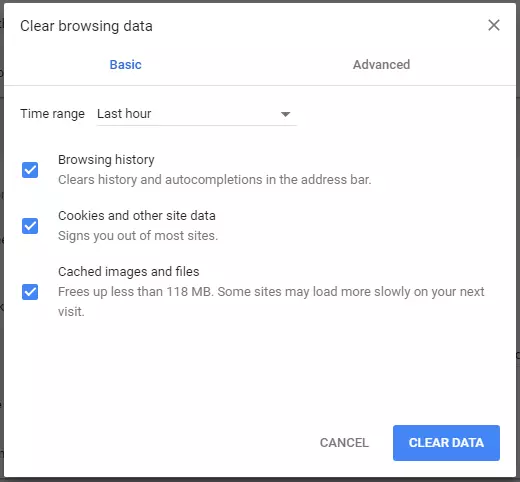
Step 3: Check the box for “Cookies and other site data” and then click “CLEAR DATA” to delete all existing cookies.
This short video shows you how to delete cookies from the Chrome browser:
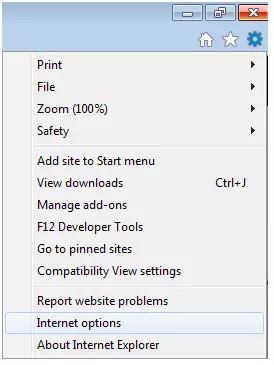
Disabling cookies in Internet Explorer
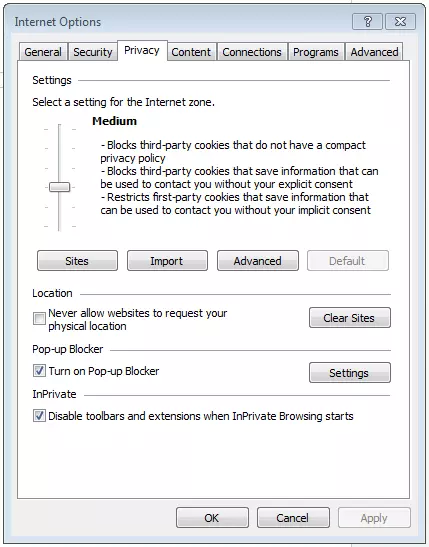
Cookie settings can be found via the “Privacy” tab. Use the slider to select a setting. As you toggle the slider, each setting is explained in detail so that you can select how strictly cookies should be blocked. Setting the slider at the top of the bar is how to block all cookies.
In Internet Explorer, “Medium” is the default setting. This setting blocks cookies from third parties that don’t have a compact privacy policy. In addition, the medium setting limits first-party cookies that can use stored information to contact you without your implicit consent. To completely disable cookies in Internet Explorer, set the slider to the top setting “Block All Cookies.”
Microsoft has discontinued the further development of Internet Explorer in favor of its successor, Microsoft Edge. Switching to this or another current browser is therefore strongly recommended for security reasons.
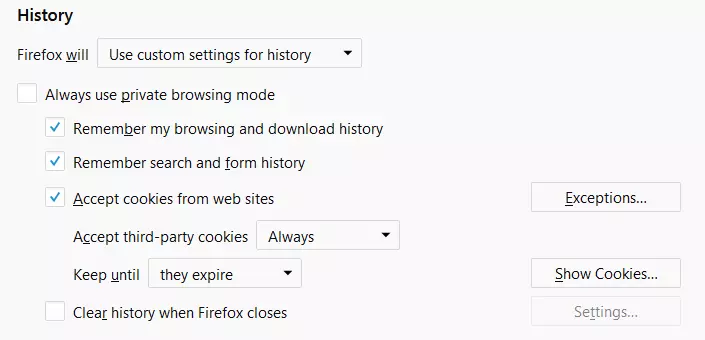
Disabling cookies in Firefox
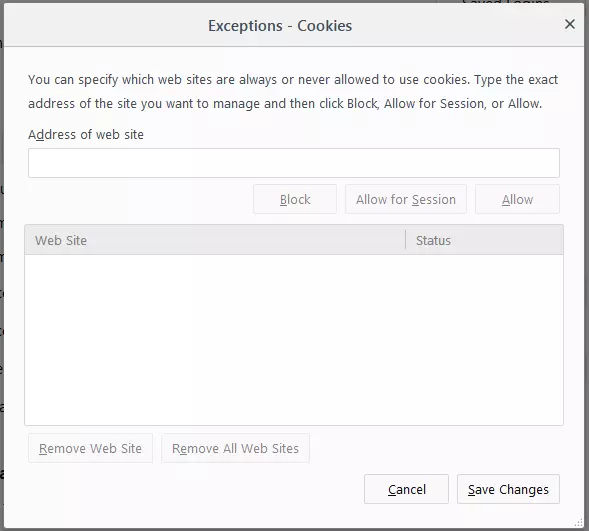
Block cookies in Firefox comprehensively by unchecking the box “Accept cookies from web sites.” The “Exceptions” button can be used to specify websites that should be allowed despite the blocked cookies setting. To do this, simply enter the relevant domains and select “Allow” or “Allow for Session.”
This short tutorial shows you how to delete cookies in Firefox:
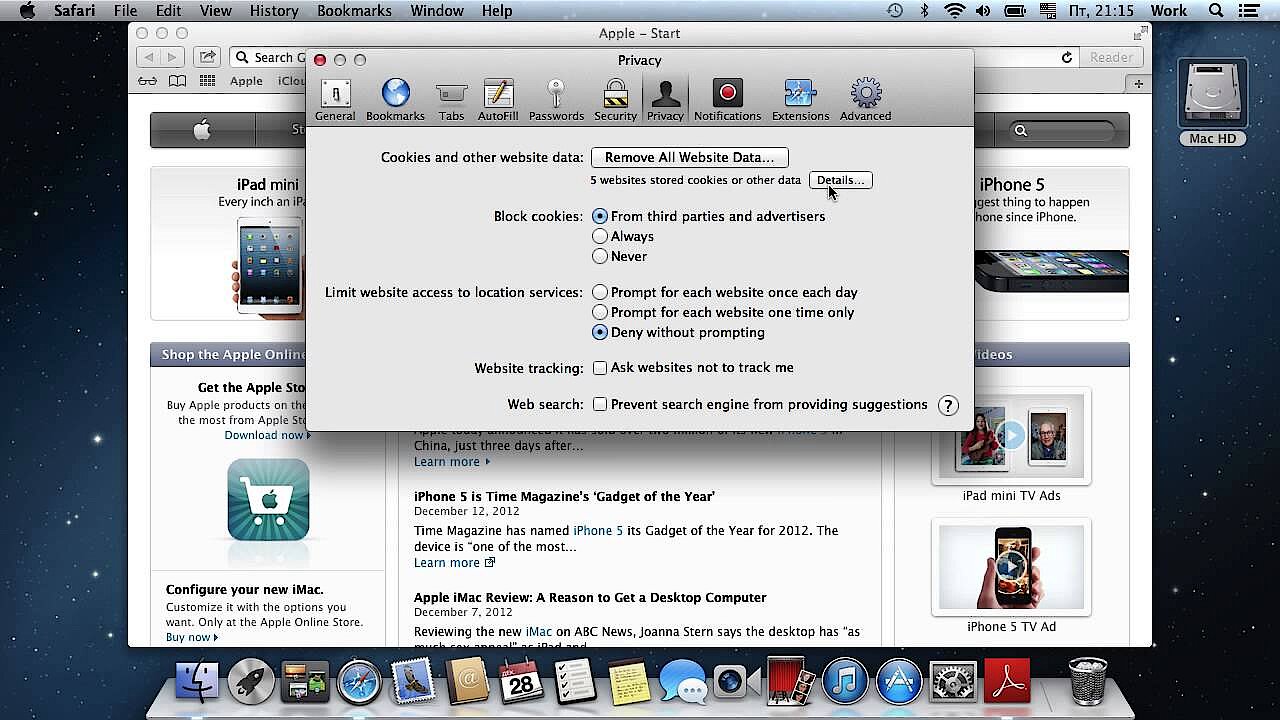
Deleting cookies in Safari
To turn off cookies in Safari, go to “Settings” via the gear button at the top right corner. A new window will open in a different tab. Choose the “Privacy” option. To block all cookies, choose “Always block” by “Cookies and website data.”
Saved cookies can also be deleted in the same section by clicking “Remove All Website Data.”
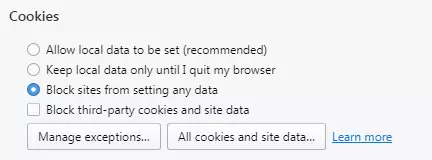
How to disable cookies in Opera
Learn how to block cookies in Opera:
Step 1: Open the settings menu by clicking the Opera symbol in the upper left corner and then select “Settings” or use the [Alt] + [P] shortcut key.
Step 2: Click “Privacy & security.”
Step 3: Block all cookies with the option “Block sites from setting any data.”
By opening the cookies list you can also choose to delete specific cookies by placing an “x” next to each individual cookie that you want to remove. On the same screen, it’s possible to delete all cookies at once. Look for the “Delete all” button above the list which allows you to remove all cookies with one click.
It’s always advisable to delete cookies after each session if the computer is shared with other users. In Opera, click “Clear browsing data…” in the “Privacy & security” menu.