WebP - Image Format for the Web
The loading speed has long been one of the most important factors when optimizing a website, with visitors as well as search engines regarding the time it takes to call up a page as an important evaluation criterion. A lean and compressed code or the use of caching mechanisms are part of the tried and tested solutions for a fast Web presence, as is the use of compressed images. The latter – as design and background elements – are included in many projects in large numbers, and their effect on the loading time is often underestimated.
The search engine giant Google among others, tackled this problem, and it presented its own license-free image format for faster websites in 2010 - WebP. But what exactly is behind the web format that arose from the video codec VP8? And how does it do in direct comparison with established variables such as JPEG?
What is WebP?
On 30 September 2010, Google announced the release of a new open standard for lossy compression of 24-bit graphics on the Web. The video format VP8 served as a model for the format with the name WebP, and this was developed by the company On2 Technologies, which Google had bought up in the same year. In the period following, Google extended the WebP format with features such as a lossless compression mode, transparency (alpha channel), and animations. Chrome has supported the compression format since the end of 2010, as has the browser Opera. But there are still a variety of browsers to date – such as Safari and Firefox – which have only supported WebP experimentally up to now, and do not offer support with their regular releases. According to its own information, Microsoft is currently working on support for its browser Edge.
You will find continuously updated information on WebP browser support at caniuse.com.
All software for the processing and presentation of WebP is under the BSD license as standard. Google uses the format, for example, in the Chrome Web Store, and in the mobile Google+ apps.
What characteristics distinguish WebP?
WebP has always served the purpose of reducing images on the Web to as small a file size as possible. According to information from Google, images and graphics in WebP format are around 30 per cent smaller than PNG or JPEG files with the same image quality. While both these classic Web formats rely on different compression methods – PNG is lossless and JPEG lossy – WebP allows both options. Thanks to this flexibility, the format is suitable for photos as well as small images and graphics. The compression features as well as the other central characteristics of the WebP format can be summarized as follows:
- Compression (lossy): Lossy compression with WebP uses keyframe coding of VP8.
- Compression (lossless): Lossless compression with WebP is based on various techniques that transform the parameters and image data. The LZ77 algorithm is also used here.
- Transparency: The 8-bit alpha channel that the WebP format offers can also be used for lossy RGB compression.
- Metadata: WebP may include EXIF and XMP metadata, which is typically generated by cameras.
- Color profile: The Google format may contain embedded ICC profiles (data sets that describe the color spectrum).
- Animations: The WebP format enables image sequences to be saved.
How does lossy WebP compression work?
Lossy compression with WebP uses the same method as the block-based VP8 codec, to predict frames – i.e. individual images. Each frame is therefore divided into smaller segments, which are also described as macro-blocks. Within these macro-blocks, the coder can predict redundant movement and color information and subtract these from the block. The result of this predictive compression consists of the remaining block information and the separate redundant information (typically including many zero values). It is quantified and entropy coded (presentation of characters through specific bit pattern). The quantification phase is the only process here in which the bits are actually discarded as lossy.
WebP relies on an arithmetic coding method that is more effective than Huffman coding which is used with JPEG, for example. Both involve forms of entropy coding. However, the Huffman method assigns a whole number of bits to each character, while the arithmetic coding of the entire character string allocates a single longer bit code. The complexity is therefore higher with the arithmetic coding, but the generation of bit location redundancies is excluded (only redundancy of complete messages).
Operating principles of lossless compression with WebP
With lossless WebP compression, the first step involves transforming the image. For this, the following techniques can be used:
| Spatial Prediction Transform | WebP uses 13 different prediction modes, which make use of the fact that neighboring pixels frequently correlate with one another. The current pixel value is predicted from already decoded pixels, and only the remaining value is coded. |
|---|---|
| Color Transform | The aim of color transform is the decorrelation of the RGB values of each individual pixel. Here the image is first divided into blocks, before red (R) is transformed based on green (G) and blue (B) based on green and red. The green value is kept as it is in the meantime. |
| Subtract Green Transform | In addition to the general color transformation, a variant is possible in which the green values are deducted from the red and blue values. |
| Color Indexing Transform | If there are too few unique pixel values, the WebP format also provides the option of color indexing transformation. The number of unique ARGB values in the image then becomes more definite, and creates allocation of these values if the number is too small. This allocation is used to replace the pixel values with the relevant index. |
| Color Cache Coding | Loss-free WebP compression can use image fragments already seen to reconstruct new pixels . If there are no suitable hits here, a local color cache with the 32 last used colors serves as a starting point here. This is continuously updated. |
The transformed parameters and image data are entropy coded, whereby a variant of the LZ77 algorithm is used. This uses small values for spatially close pixels.
What distinguishes animated WebP?
Thanks to support from animated images WebP is an appealing alternative to GIF or APNG. Strengths come into play here such as the color depth of 24 bit and the 8-bit alpha channel, as well as the high degree of compression. This enables the WebP format in contrast with the competitive formats in addition to the lossless as well as the lossy compression of the animations. Animated WebP is also convincing in terms of decoding: As WebP metadata saves whether each frame contains alpha values, the decoder does not have to convert each frame individually to receive this information.
According to Google the conversion of GIFs into lossy WebP reduces the file size by up to 64 per cent, and for lossless WebP this is still 19 per cent.
The keyframe technology of the WebP format already mentioned shows its strengths, particularly in animations, where the key frames ensure high quality. However, for this reason, the decoding process is also more CPU-intensive than for GIF, for example.
How does the development of WebP look?
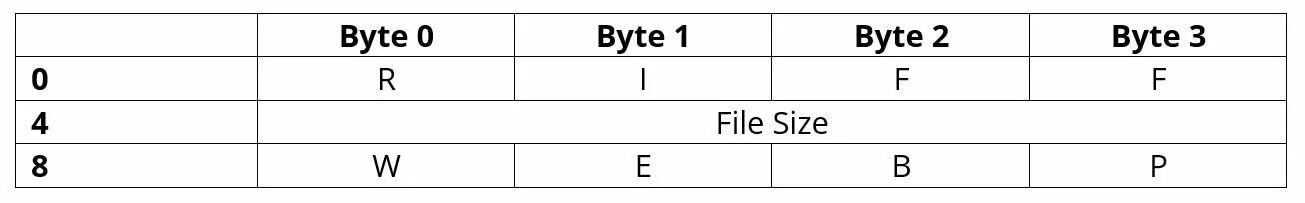
WebP files are container data, where the RIFF developed by Microsoft and IBM is relied upon as a container format: (Resource Interchange File Format). A file in WebP format therefore consists of a RIFF header and the corresponding WebP content.
The RIFF/WebP header comprises the following three 4-byte series:
- FourCC (four character code) “RIFF”: Type identifiers from the four ASCII characters R, I, F and F, which specifies that a RIFF container file is involved.
- File size: Details on the size of the file
- FourCC “WEBP“: Type identifiers from the four ASCII characters W, E, B and P, which specify that the RIFF container includes a WebP file
The header is followed by the WebP file blocks, which are also described in RIFF containers as “chunks”. Each chunk has its own header, to which the relevant information is attached. Possible blocks at the top levels are “VP8” (lossy WebP), “VP8L” (lossless WebP) and “VP8X” (extended WebP). The latter characterize WebP files with additional information such as EXIF metadata (“EXIF” chunk) or an ICCP color profile (“ICCP” chunk)) as well as animated WebP (“ANIM” chunk).
The complete development of files in WebP format looks as follows:
WebP vs. JPEG: WebP does well in comparison with the other image formats
JPEG or JPG is to the presentation of photos and large images on the World Wide Web what Google is to the world of search engines. Even a quarter of a century after its release, it is impossible to imagine the image format not being on the Web scene. The greatest advantage with regard to formats such as PNG – which is evenly distributed but predominantly used in smaller images and graphics such as logos, icons etc. – is without a doubt that JPEG ensures considerable memory saving thanks to lossy compression .
However, in this crucial detail WebP proves to be more efficient and more flexible. On the one hand, the Google format offers a lossless compression method as well as a lossy one, while on the other hand, the memory saving for images in the WebP format outperforms that for JPEG images of the same value. The fact that JPEG permits images with a maximum size of up to 65,535 x 65,535 pixels, while the limit of WebP is only 16,383 x 16,383 pixels, can be ignored in light of the field of use (Web).
The compression advantage that WebP has compared to JPEG, is lost with a very strong compression (from around a 90 per cent degree of compression). While such compressed JPEG images are nevertheless very pixelated, similar examples in the WebP format have a specific added value.
Similar to the comparison between WebP and JPEG is the comparison between WebP and GIF, where the format from Google also demonstrates convincing advantaged with regard to quality and compression. However, the problem is with the lack of support for WebP from browsers such as Firefox or Microsoft Edge. To date, users of these web browsers do not see images and animations in WebP, which is why barely any website operators rely on the format.
Basic data for the comparison of “WebP and JPEG” in table form:
| WebP | JPEG | |
|---|---|---|
| Release | 2010 | 1992 |
| File extension (s) | .webp | .jpeg, .jpg |
| Maximum resolution (in pixels) | 16,383 x 16,383 | 65,535 x 65,535 |
| Compression (lossless) | Yes | No |
| Compression (lossy) | Yes | Yes |
| Transparency (alpha channel) | Yes | No |
| RGB color spectrum | Yes | Yes |
| Animations possible | Yes | No |
| Supporting applications | limited (including Chrome, Opera, Gmail and IrfanView) | Universal |
How can WebPfiles be opened and converted?
File in WebP format cannot yet currently be opened with the usual image viewing programs from Windows, Linux and macOS If you want to view animations or images which have been coded with WebP, there are various options.
If Chrome or Opera are installed on your system, you can simply drag the file in question into an open window on either browser. As these browsers support WebP natively, you can view the content you wish to open without requiring further software. However, this solution is not very convenient – particularly if you want to view several images or animations. If you do not want to have to work with various browser windows and switching between them, it's easier to use IrfanView, a freeware picture viewer which also offers WebP support after the installation of the official plug-in package. However, the program is only available for Windows.
If you use the Wine compatibility layer, you can also install IrfanView under macOS or Linux, to open WebPfiles with the freeware program.
Furthermore, in the official WebP developer area Google offers a range of its own solutions for working with WebP – above all the libwebp library, which you can use to implement the WebP coding and decoding in your own programs. Also, the following tools are included in the free downloadable collection:
- cwebp enables the compression of an image field with the help of WebP. Possible input formats include PNG, JPEG and TIFF. In the tools options, you can define whether to use lossless or lossy compression.
- dwebp is a tool with which you can transform existing WebP files into other formats such as PNG (standard option), BMP, TIFF or PGM.
- With vwebp, Google supplies its own solution for displaying WebP images and animations based on OpenGL.
- webpmux is the decisive tool for working with extended WebP. You can create animations in WebP format, for example, with the program, or extend image files with metadata and ICC profiles.
- With gif2webp you convert existing GIF files into WebP. As with regular image compression, lossless as well as lossy coding is possible.
At ezgif.com you will also find a variety of tools for creating or converting WebP files. In contrast to Google applications, you can use these directly in the browser without installing them.