TLS vs. SSL: what is the difference?
You have probably already come across the two acronyms SSL and TLS, which are often combined as SSL/TLS. If you want to manually configure an email client or host website, for example, these terms cannot be avoided. In this article, you will learn what the differences between these two protocols are.
- Simple registration
- Premium TLDs at great prices
- 24/7 personal consultant included
- Free privacy protection for eligible domains
What does SSL and TLS mean?
SSL stands for “Secure Socket Layer” and TLS for “Transport Layer Security”. Both are encryption protocols for the internet’s transport layer. Their job is to encrypt data streams between the client and server.
If communication passes through this encrypted transport layer, an “s” is added to the end of the protocol name: http becomes https, imap becomes imaps, etc. The acronym SSL also appears in the term SSL certificate – this certificate is required if a website wants to communicate using https, which is what the vast majority of websites use today.
For more information about TLS, check out our follow-up article.
The difference between SSL and TLS
SSL was introduced in 1995. After a number of serious security vulnerabilities were discovered, the improved version 2.0 was released, followed by version 3.0 one year later. After discovering security vulnerabilities, the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force, responsible for further developing the internet) rejected SSL 3.0.
SSL 2.0 and SSL 3.0 are sometimes also called SSLv2 and SSLv3.
The TLS protocol is the successor to SSL. It was introduced in 1999 as an improved version of SSL 3.0 and was called SSL 3.1 at first. The current version is TLS 1.3 (as of 2018).
The jump from SSL 3.0 to TLS 1.0 was initially just a small one. “The differences between this protocol and SSL 3.0 are not dramatic, but they are significant enough that TLS 1.0 and SSL 3.0 do not interoperate” (RFC 2246). Compared to SSL 3.0, TLS 1.0 improved cryptographic security and application interoperability. The currently used version TLS 1.2 provides increased security against hacker attacks and allows applications much more flexibility with regard to the encryption used (cipher suites).
The current version of TLS is more secure, flexible, and efficient than its predecessor SSL. Since the acronym SSL is still much more widely known than TLS, many providers of client software, routers, and so forth use the term SSL or alternatively the combined term SSL/TLS. However, this is usually referring to the current version of TLS (i.e. TLS 1.3).
SSL or TLS – which one should you use?
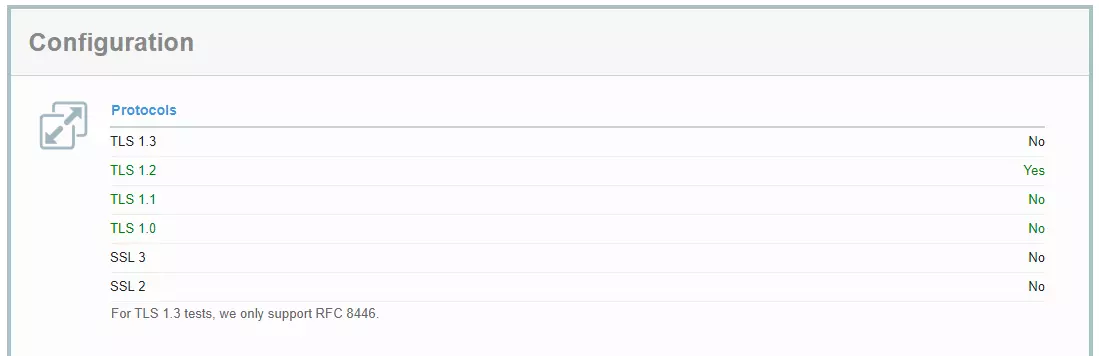
Today, the only answer is TLS. SSL 2.0 and SSL 3.0 are outdated and regarded as insecure. The same can be said about older versions of TLS. Only TLS 1.2 can still be used under certain conditions, which are outlined in the TLS 1.3 specification. However, you should avoid all SSL protocols (as using them is now prohibited) as well as TLS versions 1.0 and 1.1 (support for which will be phased out soon). On properly configured servers, these outdated protocols are disabled.
Using this GlogalSign, you can check which encryption protocols the server of a specific website has enabled.