Network types at a glance
A network is any number of independent computer systems that are interconnected so that data exchange is possible. For this to happen, networked systems must be connected logically in addition to physically. The latter is established by special network protocols, such as TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). Even just two computers connected to each other can be classified as a network.
Networks are set up to transfer data from one system to another, or to share resources, such as servers, databases, and printers on the network. Depending on the size and range of the computer network, you can differentiate between different network dimensions. The most important network types include:
- Personal Area Networks (PAN)
- Local Area Networks (LAN)
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN)
- Wide Area Networks (WAN)
- Global Area Networks (GAN)
The physical connection, which these network types are based on, can be cable-connected or implemented based on wireless technology. Physical communication networks often form the basis for several logical communication networks, so-called virtual private networks (VPNs). These use a common physical transfer medium e.g. a glass fiber cable, when transferring data and are assigned to logically different virtual networks by means of tunneling software.
Each type of network was developed for specific areas of application, is based on its own techniques and standards, and brings different advantages and limitations with it.
- Simple registration
- Premium TLDs at great prices
- 24/7 personal consultant included
- Free privacy protection for eligible domains
Personal Area Network (PAN)
To enable data exchange, modern devices such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers can be integrated into a network. This can be wired in the form of a Personal Area Network (PAN). Common transfer techniques include USB or FireWire. The wireless variety is known as Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) and is based on technologies such as Bluetooth, Wireless USB, Insteon, IrDA, ZigBee, and Z-Wave. A wireless Personal Area Network, which can be achieved via Bluetooth, is called Piconet. PANs and WPANs usually only stretch over a few meters, and are therefore not suitable for connecting devices in different rooms or even buildings.
In addition to the communication between individual devices, a Personal Area Network also makes it possible to establish a connection to other networks, usually larger ones. This is known as an uplink. Due to the limited range and a comparatively low data transfer rate, PANs are primarily used to connect peripheral devices in the hobby and entertainment sector. Typical examples include wireless headphones, game consoles, and digital cameras. Within the Internet of Things (IoT)’s framework, WPANs are responsible for the communication of control and monitoring applications with a low data rates. Protocols such as Insteon, Z-Wave, and ZigBee have been specifically designed for smart homes and home automation.
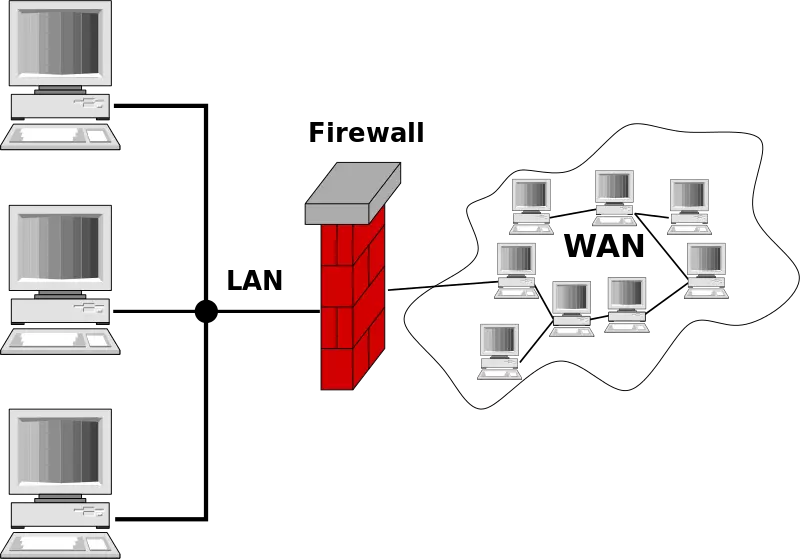
Local Area Network (LAN)
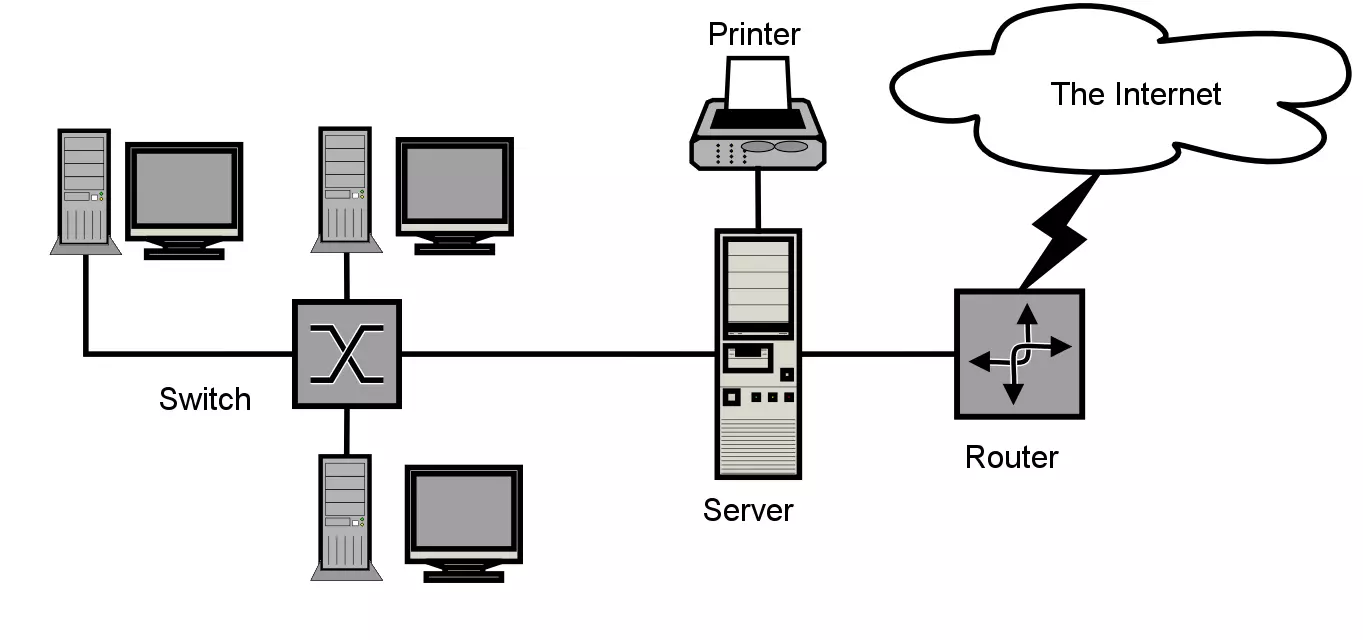
If more than one computer is to be connected to a network, this usually takes the form of a Local Area Network (LAN). Networks like these can include two computers in a private household or several thousand devices in a company. Networks in public institutionsm such as those used by public authorities, schools, or universities, are also implemented as LANs. A widely-used standard for wired Local Area Networks is Ethernet. Networking technologies such as ARCNET, FDDI, and Token Ring are less common and widely outdated. Data transmission is either electronically based on copper cables or via fiber optic cables.
If more than two computers are to be connected in one LAN, additional network components such as hubs, bridges, and switches are needed, which act as coupling elements and distribution nodes. The network type LAN was developed to enable fast transmission of large amounts of data. Depending on the structure of the network and the transmission medium used, a data throughput of 10 to 1,000 Mbit/s is normal. LANs enable convenient information exchange between the various devices connected to the network. In a business context, it’s common to share files, network printers, and applications via LAN with several computers.
If a local network is implemented via radio, it is referred to as a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). The WLAN standard’s technical basis is defined by the IEEE 802.11 family of standards. Wireless local networks offer the ability to easily integrate devices into home or corporate networks, and are compatible with wired Ethernet LANs. However, the data throughput is lower than for an Ethernet connection.
The range of a LAN depends on the standard and the transmission medium, but can be increased by signal amplifiers, known as repeaters. Regarding gigabit Ethernet via glass fibers, a signal range of several miles is possible. However, Local Area Networks rarely stretch across more than one building complex. Multiple LANs can be connected to a superior Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) or Wide Area Network (WAN).
SilverStar – Sample Network Diagram via Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a broadband telecommunication network that connects several LANs in close proximity. As a rule, these are individual establishments in a company that are connected to a MAN via leased lines. High-performance routers and high-performance fiber-based connections are used, which enable a significantly higher data throughput than the internet. The transfer speed between two remote nodes is comparable to that of communication within a LAN.
The infrastructure for MANs is provided by international network operators. As a Metropolitan Area Network, wired cities can be integrated nationally into Wide Area Networks (WAN) and internationally in Global Area Networks (GAN).
With Metro Ethernet, a special transmission technology is available for MANs, which can be used to build powerful Metro Ethernet networks (MEN) based on Carrier Ethernet (CE 1.0) or Carrier Ethernet 2.0 (CE 2.0).
A standard for larger regional radio networks, known as Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks (WMAN), was developed with IEEE 802.16. This technology known as WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) makes it possible to set up WiFi hotspots. These are several WiFi access points working together in different locations. The current transmission standard DSL is technically only available where copper cables have been laid.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
While Metropolitan Area Networks connect areas that are near each other in rural or urban areas, Wide Area Networks (WANs) extend across large geographic areas, such as countries or continents. The number of local networks or individual computers connected in a WAN is unlimited, in principle. While LANs and MANs can be implemented because of their geographical proximity to the computers and networks based on Ethernet that are to be connected, technologies such as IP/MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), PDH (Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy), SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy), SONET (Synchronous Optical Network), ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) and sometimes the outdated X.25 are used. Wide Area Networks are usually owned by an organization or company, and are operated privately or rented. In addition, internet service providers use WANs to connect local company networks and consumers to the internet.
SilverStar – Sample Network Diagram via Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0
Global Area Network (GAN)
A global network, such as the internet, is referred to as the Globe Area Network (GAN). The internet is, however, not the only computer network of its kind. Internationally operating companies also support local networks that comprise of several WANs and connect company computers across the world. GANs use the fiber optic infrastructure from wide area networks and combine these with international undersea cables or satellite transmissions.
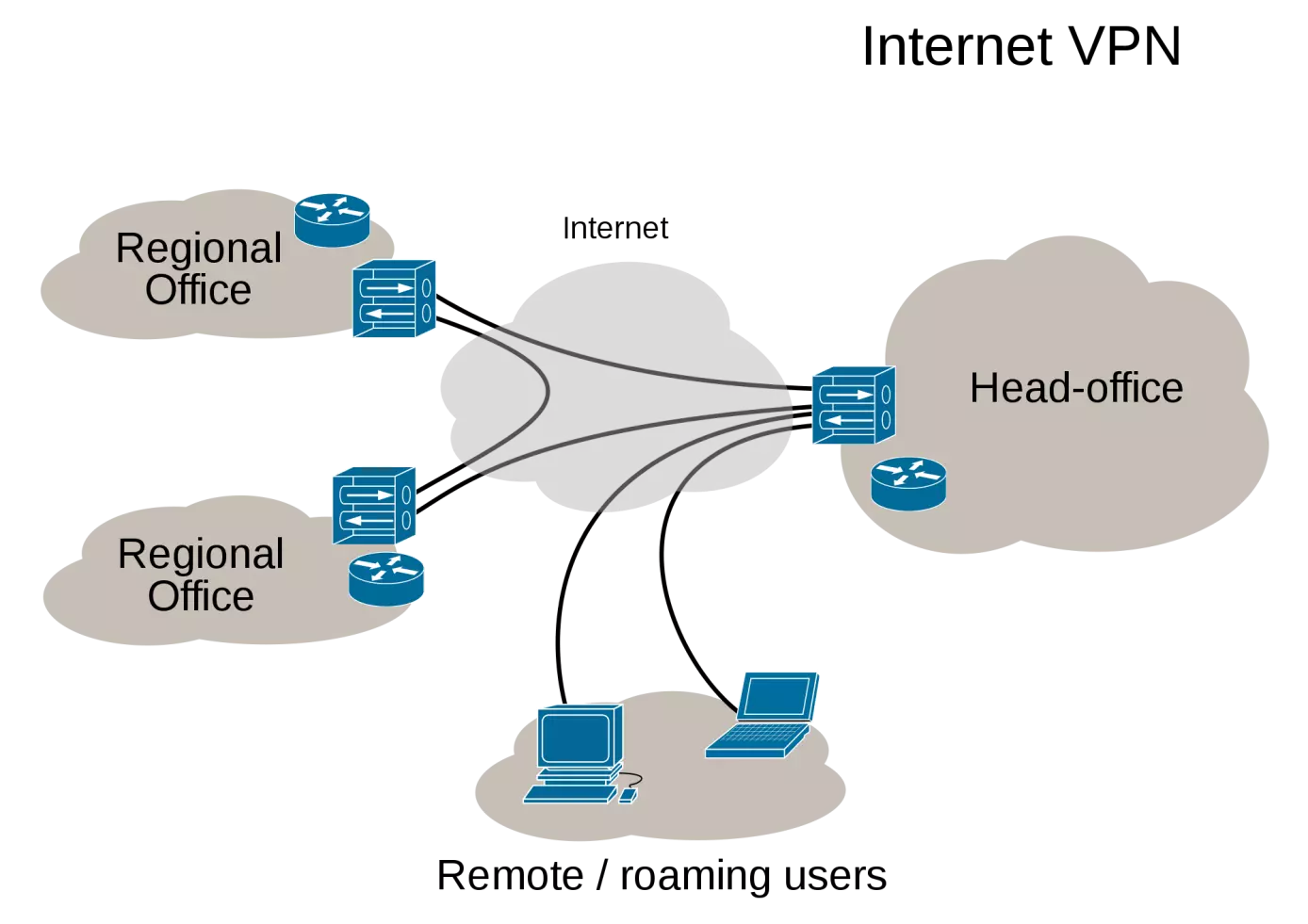
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Privat Network (VPN) is a virtual communication network that uses the infrastructure of a physical network to logically connect computer systems. This can be any of the network types introduced above, however, the internet is the most common transport medium. This connects nearly all computers worldwide and is available free of charge, as opposed to privately operated MANs or WANs. Data transfer takes place within a virtual tunnel, which is built between a VPN client and a VPN server. If the public network is used as a transport medium, Virtual Private Networks are generally encrypted to ensure that data stays confidential. VPNs are utilized to link LANs over the internet or to enable remote access to a network or a single computer via public connection.
Source: https://privacycanada.net