How to launch and use the Ubuntu task manager
Windows and Mac aren’t the only operating systems providing a task manager. Ubuntu has one too. You can open the “System Monitor” either via the [Windows] key, the Start menu or the terminal.
- Simple registration
- Premium TLDs at great prices
- 24/7 personal consultant included
- Free privacy protection for eligible domains
What is the Ubuntu task manager?
If you’re experiencing issues with your system such as slowing applications or computer functions, it’s a good idea to check what’s wrong. On a Mac or Windows, you can simply launch the Mac task manager or launch the Windows task manager to find out what’s affecting performance. Luckily, there’s a similar function available for Linux users.
While Linux distributions with graphical interfaces do not allow for system monitoring, Ubuntu does come with a task manager that lets you manage, search, filter and terminate processes if necessary. Depending on the interface, the task managers under Ubuntu may differ.
Differences between Ubuntu and Windows task managers
Though the basic options of the respective tools are similar, there are some differences between Ubuntu’s task manager and the Windows equivalent. It starts with the name. In Ubuntu, the task manager is called “System Monitor”. While the Windows shortcut [Ctrl], [Alt] + [Del] launches the task manager under Windows, using the key combination in Linux prompts a logout dialog of the GNOME desktop environment. Though right-clicking the Start icon launches the context menu under Windows, it doesn’t perform the same action in Ubuntu.
How to launch the Ubuntu task manager
You’ve got different options to launch the task manager under Ubuntu. A single universal solution for Linux doesn’t exist. Different operating systems and interfaces also have different options and processes for system monitoring. Below are the options for the most common task managers in Linux Ubuntu.
Unity
Accessing the Ubuntu task manager is particularly easy with Unity:
- Launch the application overview.
- Type “system monitor”.
- Select the program of the same name to open the task manager for Ubuntu.
Gnome
The path to access the task manager is slightly different under Gnome:
- Launch the Start menu.
- Click on “System”.
- Launch “System settings”.
- Find the Ubuntu task manager under “System Monitor”.
You can launch the task manager for Ubuntu from the terminal. To do this, use the following command:
$ gnome-system-monitorTo search for the corresponding package type “gnome-system-monitor”.
Launch via terminal
In most other systems, the easiest option to launch the task manager is via the terminal using the top command:
top [OPTION]You can use various other commands to view and manage individual processes. However, the easiest option is the top command as described above. Check the corresponding Ubuntu version to find out if commands apply to your system Some helpful commands are:
- ps: Lists current processes and is similar to the top command.
- htop: An alternative to top that needs to be manually installed before use. It has a text interface that is built on top of ncurses. Use the following command to install it:
sudo apt install htop- glances: Generate and check statistics on the individual applications in real time.
- lsof: Displays process data and lists file access.
- vmstat: Detect system overload early on and take the appropriate countermeasures.
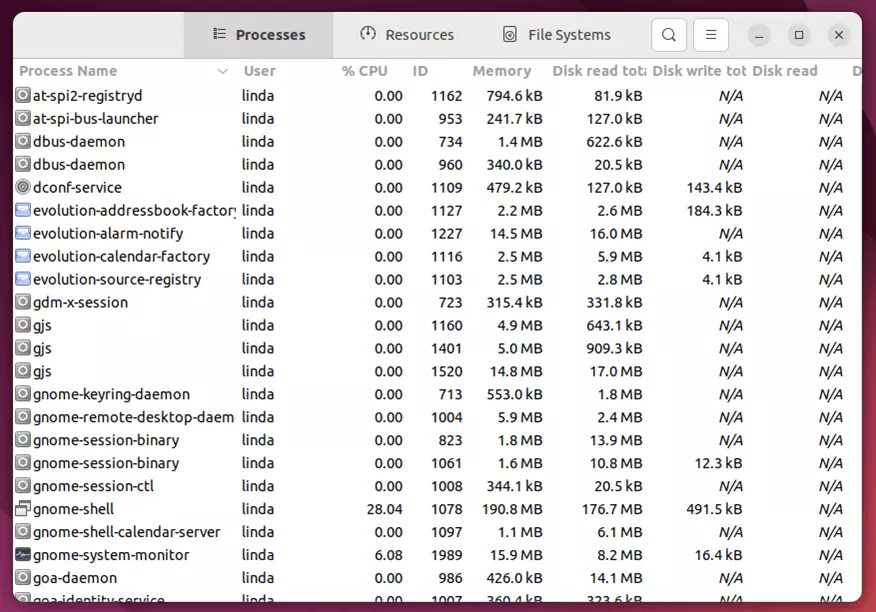
Functions of the Ubuntu task manager
- “Processes” lists the applications that are currently in use. You can terminate them if necessary.
- “Resources” displays CPU and network usage; it also lists storage capacity and outsourcing. Sorting by CPU usage is possible.
- “File Systems” displays the storage allocation of your hard disks and partitions and the type of individual file systems.
Most Ubuntu task managers include a search function to filter specific processes. In the options above, you can find the function in the bar at the top below the magnifying glass icon.
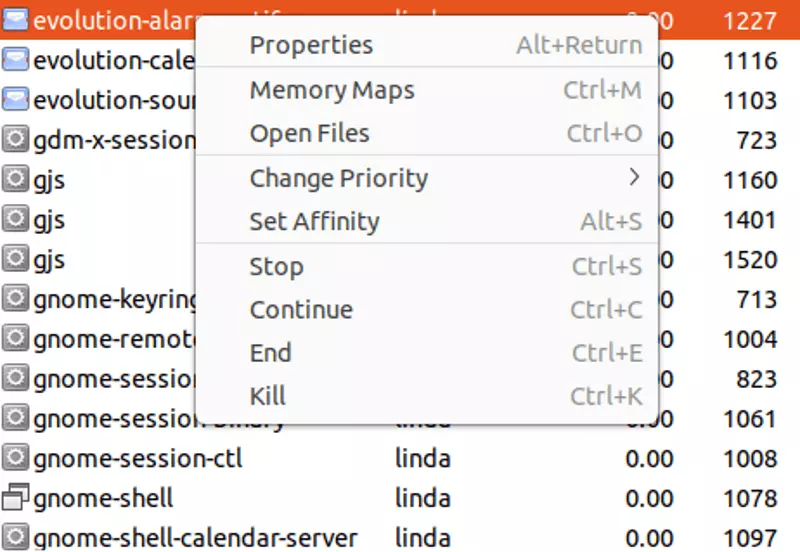
How to terminate processes
In Ubuntu, the task manager can be used to terminate problematic processes. Termination can lead to data loss. As such it’s best to terminate processes only in exceptional circumstances. System processes, however, are usually restarted and should run without problems. You can terminate processes with the task manager in Ubuntu as follows:
Step 1: Launch the Ubuntu task manager as outlined above.
Step 2: Search for the process you wish to terminate.
Step 3: Right-click on the process and a drop-down menu opens.
Step 4: You’ve now got several options. To stop the process, select “Stop”. Other options include “Pause” (and accordingly “Continue”), “Stall” or “Change Priority”.