How to Install and Configure Apache for WordPress
Combining Apache with WordPress often works without having to make any updates or changes to the web server. However, in some cases, the server application needs to be updated or configured to run WordPress. Learn how to install and configure Apache for WordPress.
What are the requirements for Apache for WordPress?
- A server running Linux
- Admin rights (root or sudo)
For cloud servers with Plesk, applications like WordPress should always be installed and managed through the Plesk interface. See our article on using WordPress on a cloud server with Plesk for step-by-step instructions.
How to check your Apache version
You can find your version of Apache using the following commands:
- Ubuntu and Debian: sudo apache2 -v
- CentOS, Fedora and RHEL: sudo httpd -v
If you run the respective command on your Linux system, you will get information about your Apache server, including the version number.
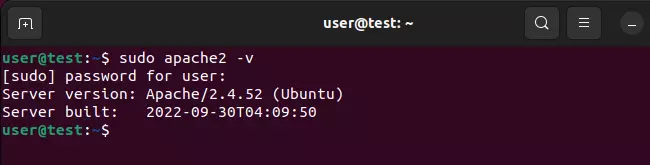
In the example above, the Ubuntu server is running Apache version 2.4.52.
Haven’t installed the web server on your Linux server yet? Read our step-by-step instructions on how to set up an Apache web server.
How to update Apache
The current version of WordPress requires Apache version 2.4 or later. This is so you can ensure that the web server is compatible with the PHP edition that is being used (7.4+). It also ensures that WordPress can fall back on the Apache mod_rewrite module. You can learn how to install PHP in our Digital Guide.
Updating Apache from version 2.2 to 2.4 may cause problems with older web software packages. Read the following list of changes carefully to ensure that your web application is not affected before upgrading Apache.
Ubuntu and Debian
On newer Ubuntu and Debian systems, including Ubuntu 22.04, install the latest version of Apache by first updating the package manager with the following command:
sudo apt updateThe next step is to use the classic Apache2 installation command to perform the upgrade:
sudo apt install apache2CentOS, Fedora and RHEL
On newer CentOS and RHEL/Fedora distributions, including CentOS 7, you can update Apache using the command:
sudo yum updateIf the command does not work, you may first need to install and set up the EPEL (Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux) package tool. On Red Hat’s official website, you can find an EPEL setup guide for RHEL and CentOS.
How to install mod_rewrite
WordPress uses Apache’s mod_rewrite rewrite engine to forward URLs and change them.
mod_rewrite is installed by default on CentOS and Red Hat systems. To install this module on Ubuntu and Debian, use the following command:
sudo a2enmod rewriteAfter installing it, you will need to restart Apache services using this command:
sudo systemctl restart apache2You then regulate URL rewrites via a .htaccess file.
- Create & customize your site with AI tools made for everyone
- 3x faster: SSD, caching & more
- Daily security scans, DDoS protection & 99.98% uptime
How to enable mod_rewrite in Apache
In some cases, you need to configure Apache in order for mod_rewrite to be executed. For this, the Apache configuration file must be adapted accordingly. The specific file will depend on your server’s web hosting setup. By default, the main Apache configuration file for your server’s primary domain is:
- RHEL, Fedora and CentOS:
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf - Ubuntu and Debian:
/etc/apache2/apache2.conf
There may also be separate Apache configuration files for each individual domain. These are usually found at:
- RHEL, Fedora and CentOS:
/etc/httpd/conf.d/[your domain name].conf - Ubuntu and Debian:
/etc/apache2/sites-available/[your domain name].conf
Once you have found the location of the configuration file, open it with any text editor (administrator access) and look for the following:
AllowOverride None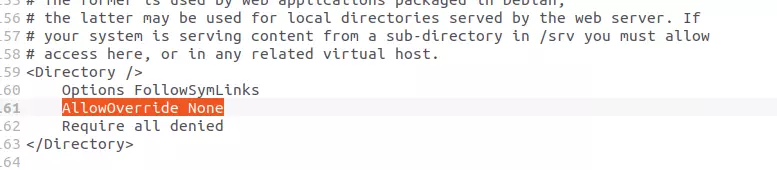
Now replace the entry with the following:
AllowOverride All
Order allow,deny
Allow from allSave and exit the file, then restart Apache with the command:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
